From Ceramics to Metals: A Guide to Materials in Thermal Spraying

Introduction
Thermal spraying is a versatile and effective surface engineering technique used to apply coatings to various substrates. These coatings enhance the properties of the base material, providing benefits such as corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and thermal insulation. One crucial aspect of thermal spraying is the choice of materials used in the process. The selection of thermal spraying materials plays a pivotal role in determining the performance and longevity of the coated surfaces.
What is Thermal Spraying?
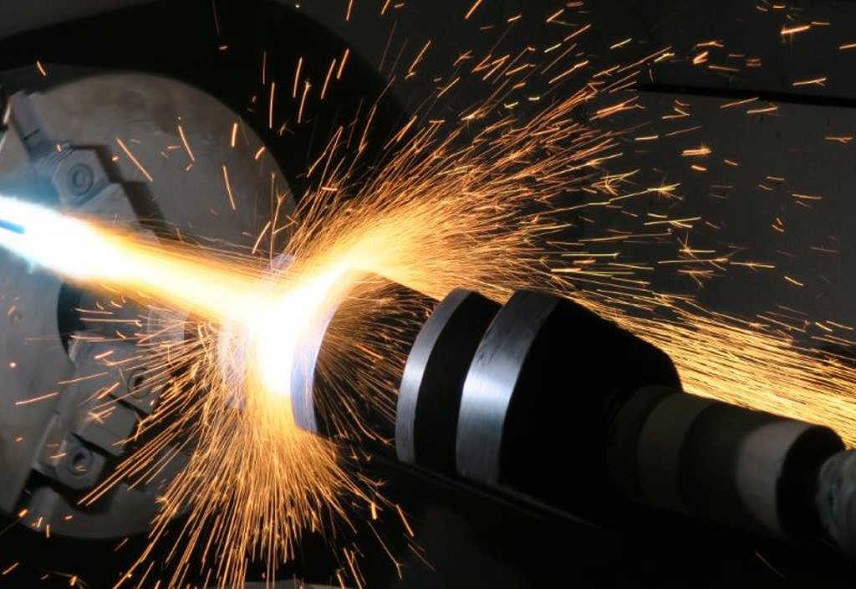
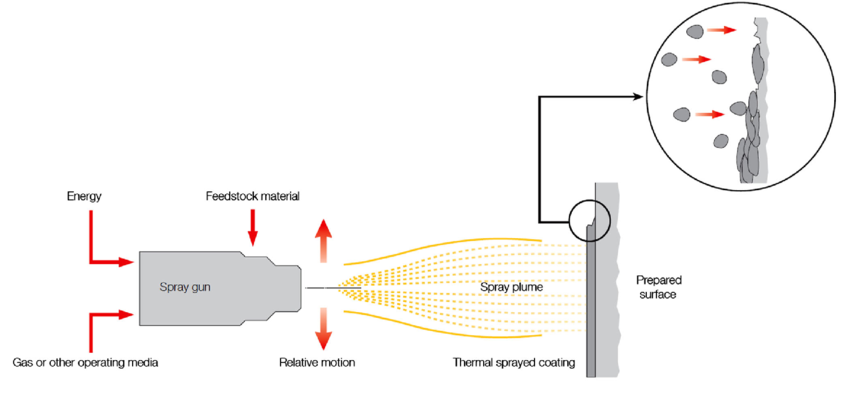
Thermal spraying, also known as metalizing or spray welding, is a process where a material in powder or wire form is heated to a molten or semi-molten state and then sprayed onto a substrate. The substrate, often a metal or ceramic component, can range from large industrial machinery to small intricate parts. The sprayed material solidifies upon contact with the substrate, forming a coating that improves the substrate's properties.
This technique is widely employed in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, energy, and electronics, due to its ability to provide cost-effective solutions for surface enhancement and protection. Thermal spraying offers advantages such as the ability to coat complex shapes, compatibility with a wide range of materials, and the ability to apply coatings with unique properties.
Gonzalez, R. & Ashrafizadeh, Hadis & Lopera, A. & Mertiny, Pierre & Mcdonald, André. (2016). A Review of Thermal Spray Metallization of Polymer-Based Structures. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology. 25. 10.1007/s11666-016-0415-7.
The Choice of Thermal Spraying Materials is Important
Selecting the appropriate thermal spraying material is critical to achieving the desired performance characteristics of the coated surface. Different materials offer distinct properties, making them suitable for specific applications. The choice of materials depends on factors such as the operating environment, required functionality, and the characteristics of the substrate. In this article, we will explore some of the most commonly used thermal spraying materials, categorized into ceramics and metals.
The Most Popular Thermal Spraying Materials
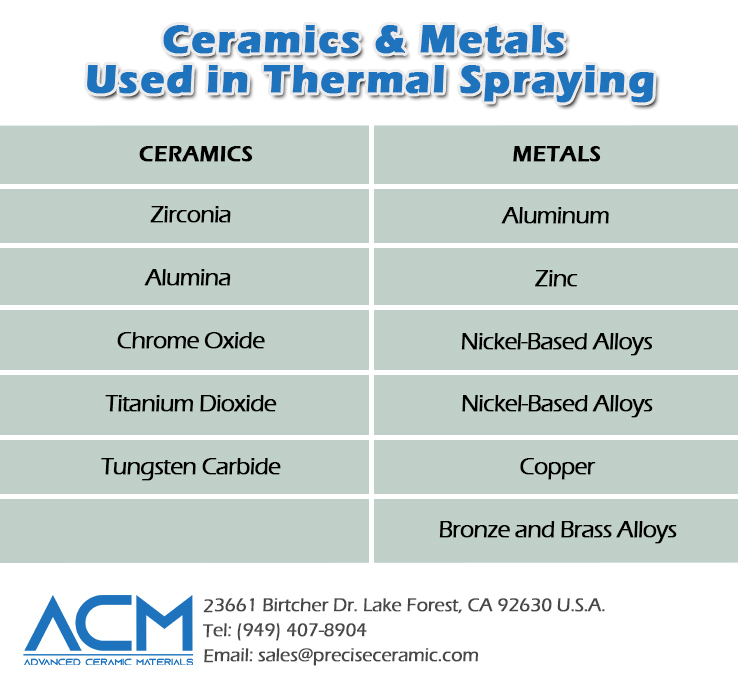
Ceramics:
Ceramic materials are known for their excellent thermal and wear resistance, making them suitable for applications where harsh operating conditions are present. Some commonly used ceramics in thermal spraying include:
a. Zirconia:
Zirconia is renowned for its high thermal expansion resistance and wear resistance. It is often used in applications where thermal barrier coatings are required, such as in turbine blades in aerospace engines. Zirconia coatings create a protective barrier that insulates the substrate from extreme temperatures, improving the overall performance and longevity of the coated component.
b. Alumina (Aluminum Oxide):
Alumina is widely utilized for its excellent wear resistance and is commonly applied in situations where abrasive wear is a concern. The automotive and manufacturing industries frequently use alumina coatings to protect components subjected to intense friction and abrasion. These coatings extend the lifespan of critical parts, reducing maintenance costs and downtime.
c. Chrome Oxide:
Chrome oxide coatings offer corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability, making them suitable for demanding environments. Industries such as aerospace and power generation often rely on chrome oxide coatings to protect components exposed to extreme conditions. These coatings provide a durable shield against corrosion, ensuring the longevity of crucial machinery and equipment.
d. Titanium Dioxide:
Titanium dioxide is chosen for its photocatalytic properties and corrosion resistance. This material is commonly used in outdoor applications where exposure to sunlight and environmental factors is prevalent. Titanium dioxide coatings provide an added layer of protection, preventing corrosion and degradation of surfaces over time.
e. Tungsten Carbide:
Tungsten carbide is renowned for its exceptional hardness and wear resistance. In thermal spraying, tungsten carbide coatings are applied to enhance the wear resistance of surfaces exposed to abrasive conditions. This material finds applications in various industries, including mining, oil and gas, and manufacturing, where protection against abrasion is crucial for equipment longevity.
Metals:
Metals are another category of materials extensively used in thermal spraying, offering a wide range of properties suitable for different applications. Some commonly used metal thermal spraying materials include:
a. Aluminum:
Aluminum is widely used for corrosion protection due to its ability to form a protective oxide layer. Additionally, it is employed in thermal barrier coatings for certain applications. The aerospace industry frequently utilizes aluminum coatings to enhance the corrosion resistance of aircraft components, ensuring their reliability and safety.
b. Zinc:
Zinc is commonly used for corrosion protection, particularly in the form of zinc coatings through processes like galvanizing. Zinc coatings provide a sacrificial layer that corrodes preferentially, protecting the underlying substrate from corrosion. This is widely employed in industries such as construction, automotive, and infrastructure to prevent rust and extend the life of structures and components.
c. Nickel-Based Alloys:
Nickel-based alloys are known for their excellent corrosion resistance and are often chosen for applications requiring high-temperature resistance. These alloys find extensive use in the aerospace and petrochemical industries, where components are exposed to harsh environments. Nickel-based alloy coatings ensure the longevity of critical parts, even under extreme conditions.
d. Cobalt-Based Alloys:
Cobalt-based alloys are selected for their impressive wear resistance and high-temperature capabilities. These coatings are commonly used in aerospace and industrial applications where components experience intense wear and elevated temperatures. The robust nature of cobalt-based alloy coatings enhances the durability and performance of coated surfaces.
e. Copper:
Copper is chosen for its electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance. In applications where both electrical and corrosion protection are required, copper coatings are often applied. The electronics industry, in particular, benefits from copper coatings on components that demand reliable electrical performance and resistance to environmental factors.
f. Bronze and Brass Alloys:
Bronze and brass alloys are utilized for their combination of wear resistance and decorative properties. These coatings find applications in various industries, including architecture and art, where aesthetics are as crucial as functionality. Bronze and brass coatings not only protect against wear but also add an attractive finish to coated surfaces.
Conclusion
Thermal spraying is a valuable technique for enhancing the properties of surfaces, and the choice of materials plays a pivotal role in its success. Ceramics and metals each offer unique properties that cater to specific application requirements. From zirconia's thermal barrier capabilities to tungsten carbide's exceptional wear resistance, and from aluminum's corrosion protection to nickel-based alloys' high-temperature resistance, the diversity of thermal spraying materials ensures a solution for various challenges.
Understanding the characteristics and applications of different thermal spraying materials empowers industries to make informed decisions when selecting coatings for their components. Whether aiming to improve wear resistance, enhance corrosion protection, or provide thermal insulation, the right choice of materials in thermal spraying can significantly contribute to the longevity and performance of coated surfaces across diverse sectors. As technology continues to advance, the field of thermal spraying will likely see further innovations in materials and applications, reinforcing its position as a crucial process in the realm of surface engineering.
At Advanced Ceramic Materials (ACM), we take pride in being a leading supplier of high-quality ceramic materials for thermal spraying. Contact us today to explore our comprehensive product range and benefit from our expertise in providing innovative solutions for your thermal spray challenges.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}
LEAVE A REPLY
SUBSCRIBE OUR NEWSLETTER
- How PBN Crucibles Ensure the Quality of GaN & SiC Epitaxial Materials
- SiC vs. Quartz Focus Rings: A Cost and Performance Analysis for Advanced Etch
- AlN Ceramic Substrates: Enabling Next-Gen Electrostatic Chucks
- The Amor of Semiconductor Tools: Why High-Purity Al2O3 & AlN Are Preferred for Plasma Process Chambers
- Silicon Carbide - Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics for Extreme Environments