Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN)
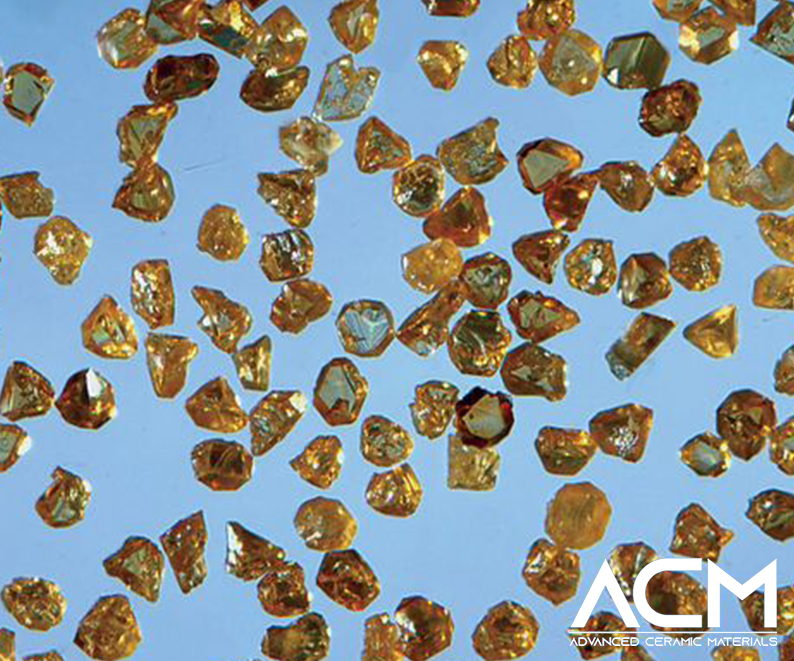
Cubic Boron Nitride (cBN), belonging to the boron nitride material family, is second only to diamond in hardness and is particularly favored for its use in abrasive and cutting tool applications due to its unique combination of high abrasion resistance, superior thermal conductivity, and remarkable chemical stability at elevated temperatures. This synthetic crystalline material distinguishes itself from diamond by its ability to retain structural integrity and resist graphitization at temperatures up to 1400°C, making it more suitable for processing ferrous materials. Its chemical inertness, especially towards iron and steel at high temperatures, positions cBN as an indispensable material for high-temperature machining and grinding operations, where it outperforms traditional abrasives.
CBN's exceptional properties, including its thermal stability and high thermal conductivity, are crucial for efficient heat management during intensive industrial tasks, enhancing tool longevity and performance. As a standout member of the boron nitride family, cBN's wear resistance and ability to maintain hardness under thermal stress make it a preferred choice for the development of durable, high-performance industrial tools and components. These attributes ensure cBN's pivotal role in applications demanding maximum durability, effective thermal management, and chemical resistance, solidifying its status as a critical material in advanced manufacturing processes.
More Info About Cubic Boron Nitride
Products | Structure | Specification | Applications | Video | FAQs
Cubic Boron Nitride Structure
Cubic Boron Nitride (cBN) possesses a crystalline structure that closely resembles that of diamond, making it one of the hardest materials known. This structure is characterized by a cubic lattice in which boron and nitrogen atoms are alternately situated, similar to the carbon atoms in diamond. This arrangement allows for the strong covalent bonding between boron and nitrogen atoms, providing cBN with its exceptional hardness and thermal stability.
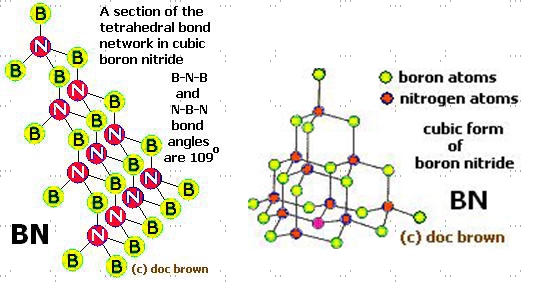
The cubic structure of cBN is responsible for its high resistance to wear and thermal shock, making it ideal for cutting and abrasive applications, especially in environments where materials are subjected to high temperatures and pressures. Unlike diamond, cBN does not convert to graphite under high temperatures, maintaining its integrity and properties up to about 1400°C in air. This stability, combined with its chemical inertness, especially to ferrous materials, makes cBN an invaluable material in industrial processes involving high-speed machining, grinding of hard materials, and applications demanding high durability and resistance to thermal and chemical degradation.
Cubic Boron Nitride Specification
| Physical Properties | |
| Chemical Formula | BN |
| Density (g/cm3) | 3.48 |
| Color | Typically transparent to pale yellow |
| Crystal Structure | Cubic |
| Mechanical Properties | |
| Hardness (Vickers) | 4500 kg/mm² |
| Compressive Strength MPa @ R.T. | 3,800 |
| Modulus of Elasticity (Young's Mod.) Gpa | 700-800 |
| Electrical Properties | |
| Dielectric Constant 1MHz @ R.T. | ~7.0 (varies by purity) |
| Electrical Resistivity Wcm @ R.T. | >10^16 |
| Thermal Properties | |
| Thermal Conductivity W/m-K @ R.T. | 200-700 (highly dependent on orientation and purity) |
Cubic Boron Nitride Applications
Cubic Boron Nitride (cBN) is a superabrasive material with a wide range of industrial applications due to its exceptional hardness, thermal conductivity, and chemical stability. Below are key applications of cBN:
Cutting and Machining Tools
Hardened Steels: cBN is extensively used for machining hardened steels, offering high resistance to wear and maintaining sharpness longer than conventional tools.
High-temperature Alloys: It's ideal for cutting nickel-based and cobalt-based superalloys, commonly used in aerospace and energy industries, due to its thermal stability.
Abrasives
Grinding Wheels: cBN grinding wheels are preferred for their ability to grind tough materials with precision and minimal heat generation.
Polishing Tools: In precision polishing, cBN is used for its uniform abrasion, ensuring high-quality surface finishes on metals and alloys.
Electronics
Heat Sinks and Substrates: The high thermal conductivity of cBN makes it suitable for heat sinks and substrates in electronic devices, effectively dissipating heat and improving device performance.
Wear Parts
Bearings and Seals: cBN's hardness and wear resistance make it a material of choice for bearings and seals in machinery exposed to high stress and abrasive conditions.
Aerospace and Defense
Protective Coatings: cBN coatings protect components against wear and thermal degradation in harsh environments, such as in jet engines and missile systems.
Automotive
Brake Discs and Engine Components: The high thermal conductivity and wear resistance of cBN contribute to the manufacturing of durable brake discs and engine components that withstand high temperatures and stress.
ACM Ceramic Product Video
Your CBN Ceramics Supplier
Advanced Ceramic Materials is a leading supplier of cubic boron nitride ceramic products of the highest quality for a wide range of applications. We are happy to provide advice on materials, design, and application. Feel free to contact us with any questions about CBN or other ceramic materials that are not listed on the website.
| Chemical Formula | BN |
| Mechanical | |
| Density | 3.48 g/cm3 |
| Hardness | 45-50 GPa |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 850-900 GPa |
| Flexural Strength | 500-600 MPa |
| Compressive Strength | 3500-4000 MPa |
| Poisson's Ratio | 0.1-0.2 |
| Fracture Toughness | 6-7 MPa m½ |
| Electrical | |
| Dielectric Strength | - |
| Dielectric Constant | - |
| Volume Resistivity | 10^8 - 10^9 Ω·m |
| Thermal | |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 4.7 x 10^-6 /°C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 400-1000 W/(m*K) |
| Specific Heat | 0.5 J/g·K |
| Shock Resistance | - |
| Maximum Working Temperature | 1500℃ |