An Introduction to Lanthanum Hexaboride

What Is Lanthanum Hexaboride?
Lanthanum hexaboride ((lanthanum boride, or LaB6)) is an inorganic non-metallic compound composed of low-valence boron and the rare metal element lanthanum. It is a refractory ceramic that could withstand high temperatures and harsh environments. Lanthanum hexaboride ceramic has found lots of applications because of its ideal thermal, chemical, and electronic properties.
 [1]
[1]
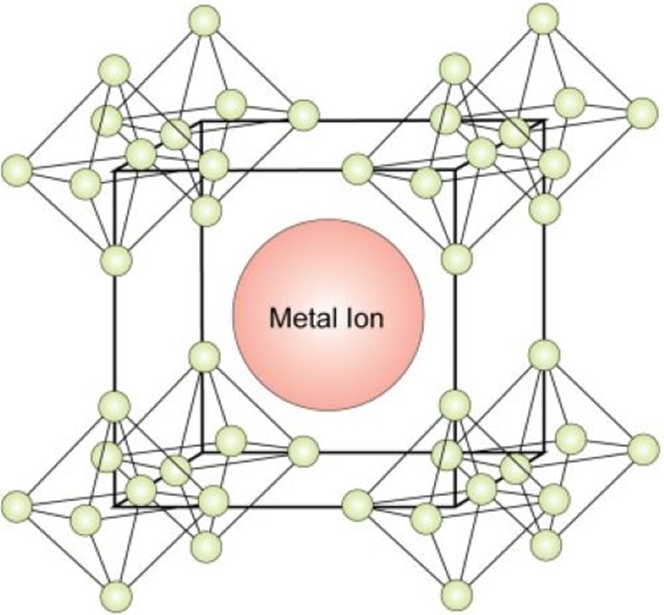
Figure 1. Lanthanum Hexaboride Structure
Lanthanum hexaboride stands out for its crystal structure (See figure 1). Inside the cubic lattice, the lanthanum atom locates at the center, while eight octahedral boron atoms sit symmetrically in the corner of the cube and surround the metal atom. There is no valence bond between the metal atom and the boron atoms, while the boron atoms are bonded to each other.
Properties of Lanthanum Hexaboride
This special structure brings about the following features of lanthanum hexaboride.
- Physical Properties: Lanthanum hexaboride looks purple-violet. It is insoluble in water and hydrochloric acid. Because the covalent bonds between boron atoms are extremely strong, LaB6 has a high melting point of 2210 °C. It also has a Mohs hardness of 9.5, while the hardness of a diamond is 10.
- Chemical Stability: Lanthanum hexaboride possesses good chemical and oxidation resistance. This stable material does not react with water, oxygen, or even hydrochloric acid. It only reacts with nitric acid and aqua regia at room temperature. Oxidation occurs at 600-700°C in an aerobic atmosphere.
- Electron Emissivity: LaB6 is an exemplar trivalent hexaboride. Inside the crystal, the boron sub-lattice is deficient in electrons and gets electrons from the metal atom. So, the hexaboride obtains a low work function of about 2.5 eV and the highest electron emissivity.
- Other Characteristics: LaB6 is a superconductor, and the transition temperature is 0.45 K. Besides, it is a solar absorber with an intrinsic low thermal emittance and good spectral selectivity.
Preparation of Lanthanum Hexaboride
There are several advanced techniques to produce lanthanum hexaboride.
- Solid-state Reactions
Solid-state reactions are divided into two steps: mixing and purification. Initially, high-purity lanthanum compounds are mixed with boron and heated at elevated temperatures up to 1200 K. Purification follows. H, C, O, N, and B elements are removed using excess boron, carbon, and B4C.
- Electrolysis and Flux
These two techniques are used to grow crystals in a molten bath. They employ a bath of molten salts to dissolve the metal and boron. The ions obtained deposit on the cathode and crystallize.
- Vapor Deposition or Metal-gas Reactions
These approaches generally synthesize nano-structured materials such as nanowires, nano bars, and nano obelisks. Among them, PVD is a non-reactive method that makes thin films and coatings of lanthanum hexaboride.
Applications of Lanthanum Hexaboride
Lanthanum hexaboride is mainly used to manufacture thermionic emitters (or hot cathodes). These cathodes can be crystals or coatings. Hexaborides have low work functions and the highest electron emissivity, which makes them ideal choices for electron emitters. Thus, they are used to make electron guns, which are an indispensable part of scanning electron microscopes, transmission electron microscopes, and electron lithography systems.
Take the case of scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Figure 2 shows the internal structure of an SEM detector. The LaB6 cathode emits electrons, while the anode receives electrons. At last, we would get a detailed image manifesting the texture, arrangement, and chemical components of the solid specimen.
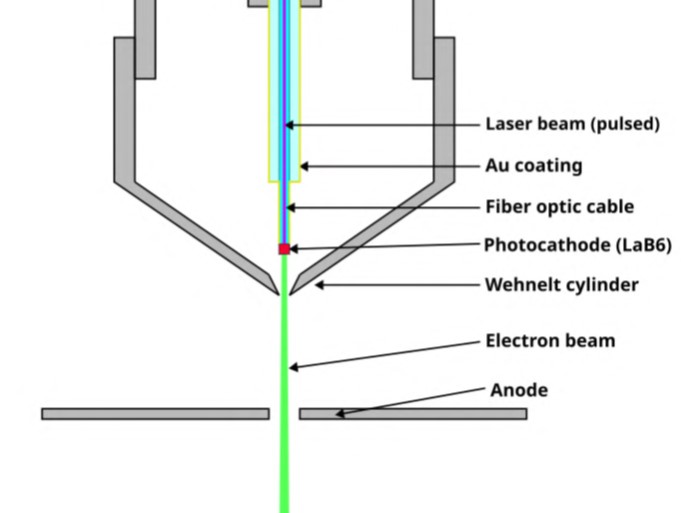
Figure 2. Lanthanum Hexaboride Cathode Structure
You can also find LaB6 products used in households and businesses. Lanthanum hexaboride is a promising superconductor and solar absorber as we mentioned above. Additionally, it is employed as an additive to enhance materials’ oxidation resistance at extreme temperatures. It is also a popular material for plasma sources for plasma-enhanced coating (PECVD) since it has s well-defined plasma reflection edge.
Related reading: Features and Applications of LaB6 Filaments
Conclusion
Because of outstanding chemical stability, electron emissivity, and superconductivity, lanthanum hexaboride is applied to produce electron microscopes, superconductors, and other useful tools. Advanced Ceramic Materials (ACM) has lanthanum boride ceramic, crystals, and cathodes. If you have any other questions about lanthanum hexaboride and other advanced ceramic materials, please check our homepage.
Reference:
[1] James T. Cahill, Olivia A. Graeve, (2019). Hexaborides: A review of structure, synthesis and processing [Photograph]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2238785418311062#fig0005
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}
LEAVE A REPLY
SUBSCRIBE OUR NEWSLETTER
- How PBN Crucibles Ensure the Quality of GaN & SiC Epitaxial Materials
- SiC vs. Quartz Focus Rings: A Cost and Performance Analysis for Advanced Etch
- AlN Ceramic Substrates: Enabling Next-Gen Electrostatic Chucks
- The Amor of Semiconductor Tools: Why High-Purity Al2O3 & AlN Are Preferred for Plasma Process Chambers
- Silicon Carbide - Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics for Extreme Environments