Stabilized Zirconia Used in Oxygen Sensor
What Is an Oxygen Sensor?
Introduction
An oxygen sensor is an electronic device that measures the air-fuel ratio in gas or liquid. It is also called lambda sensor since lambda means air-fuel ratio. The first sensor was made of zirconia ceramic with platinum coatings by Dr. Günter Bauman of Robert Bosch GmbH in the late 1960s. Over time, a variety of oxygen sensors has entered the market after development, but the zirconia oxygen sensor remains to be one of the most commonly used sensing devices in the market. Advanced Ceramic Materials (ACM) is a leading supplier of zirconia. We offer consumers high-quality zirconia of different shapes and configurations.
Two Types of Oxygen Sensors
The oxygen sensor can be divided into two common types according to their different operating principles.
- Electrolyte sensors: The electrolyte sensor measures the proportion of oxygen using electrodes. Generally, there is a cathode and an anode submerged in an electrolyte. Once oxygen enters the device, it is reduced at the cathode, and an electric current is created.
- Semiconductor sensors: The semiconductor sensor measures the oxygen concentration with optical equipment. Basically, a chemical film is tied to an optical cable, and the film’s fluorescence features are linked with the proportion of oxygen.
What is Zirconia Oxygen Sensor?
Excellent Properties of Zirconia
Zirconium oxide (ZrO2), commonly known as zirconia, is a stable ceramic material used in refractories, biomaterials, oxygen sensors, etc. Zirconia could be divided into three types. Under normal conditions, the monoclinic structure could be obtained. When the temperature rises to 1240 °C, it turns into a tetragonal structure. The last cubic type could be obtained at 2370 °C. The tetragonal (partially or totally stabilized) zirconia is an ideal conductor for oxygen ions, so it has been used in electrolyte sensors for years. Further Reading: Applications of Zirconium Dioxide
How Does the Sensor Work?
Zirconia oxygen sensor is a type of solid electrolyte sensor widely used in a range of applications. It employs two zirconia electrodes with a thin platinum coating and provides an output voltage according to the proportion of oxygen in the atmosphere. Zirconia oxygen sensor functions according to the following principles. At high temperatures (higher than approximately 316 °C /600 °F), stabilized zirconium oxide serves as an electrolyte. The oxide partly dissociates and produces oxygen ions. These ions travel through the material and a voltage (Nernst voltage) is generated across it. This voltage is related to the oxygen concentration inside.
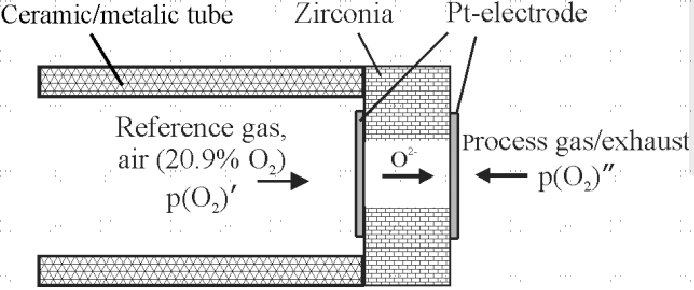
Shuk, Pavel. (2010). Process Zirconia Oxygen Analyzer — State of Art Zirkondioxid-Sauerstoffsensoren — Stand der Technik. Tm-technisches Messen. 77. 19-23. 10.1524/teme.2010.0003.
What Are the Applications of Zirconia Oxygen Sensors?
Zirconia oxygen sensors are used in numerous fields to measure the air-fuel ratio. The most common application is to measure the oxygen proportion of internal combustion engines in cars and vehicles, so the fuel could be burned more properly, and the converter could perform optimally. The ideal output voltage of approximately 0.45 V (450 mV) DC represents an ideal mixture of oxygen and fuels. Zirconium oxide oxygen sensors have other industrial uses as listed below:
- Zirconia oxygen sensors are used in oxygen analyzers in medical applications like anesthesia monitors, respirators, and oxygen concentrators.
- Divers use oxygen sensors (or ppO2 sensors) to measure the partial pressure of oxygen in their breathing gas. When it changes, divers need to stay within acceptable bounds.
- Zirconia oxygen sensors are used in hypoxic air fire prevention systems to control the oxygen proportion inside the protected volumes.
Conclusion
Zirconia is chemically inactive and has a high melting point and high resistivity. It is used in oxygen sensors because the stabilized zirconium dioxide (ZrO2) will be partially dissociated to produce mobile oxygen ions Advanced Ceramic Materials (ACM) is a leading global supplier. We have over two decades of experience in the manufacture, sale, and other commercial uses of zirconium oxide. Visit our site to get more information about high-quality zirconium oxide products for your R&D and production needs.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}
LEAVE A REPLY
SUBSCRIBE OUR NEWSLETTER
- How PBN Crucibles Ensure the Quality of GaN & SiC Epitaxial Materials
- SiC vs. Quartz Focus Rings: A Cost and Performance Analysis for Advanced Etch
- AlN Ceramic Substrates: Enabling Next-Gen Electrostatic Chucks
- The Amor of Semiconductor Tools: Why High-Purity Al2O3 & AlN Are Preferred for Plasma Process Chambers
- Silicon Carbide - Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics for Extreme Environments