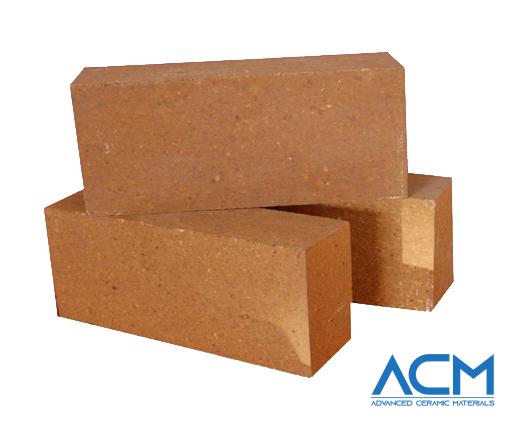
AC6250 Phosphate Bonded High Alumina Brick
- Catalog No. AC6250
- Material Al2O3, SiC, SiO2
- Bulk Density 2.65 g/cm3
- Content Al2O3 ≥50%
- Max Working Temp. 1300℃
Inquiry
AC6250 Phosphate Bonded High Alumina Brick
Overview of Phosphate Bonded High Alumina Brick
Phosphate Bonded High Alumina Bricks are a specialized type of refractory brick formulated with high alumina materials and bonded using phosphate as the binder. Known for their remarkable thermal stability, these bricks also offer high mechanical strength and substantial resistance to chemical corrosion. They perform particularly well in environments with acidic to mildly basic conditions, making them highly versatile for various industrial applications.
Phosphate Bonded High Alumina Brick Specifications
|
Item |
KYPA-75 |
|
Al2O3, % |
75 |
|
ZrO2, % |
2.1 |
|
Refractoriness, ℃ |
1770 |
|
Bulk Density, g/cm3 |
2.75 |
|
Cold Crushing strength MPa |
75 |
|
0.2 MPa R.U.L ℃ |
1300 |
|
Thermal expansion coefficient (1100℃) |
20 |
Applications of Phosphate Bonded High Alumina Bricks
- Metallurgical Furnaces: These bricks are commonly used in high-stress components of metallurgical setups, such as blast furnaces and ladles, where they withstand extreme temperatures and resist slag erosion.
- Cement Kilns: Ideal for lining cement rotary kilns and mineral calcination kilns, these bricks offer durability and stability under continuous high-temperature conditions.
- Incinerators and Waste Processing Facilities: Their high resistance to temperature fluctuations and chemical corrosion makes them suitable for incinerators and waste treatment plants, where they endure intense heat and chemical wear.
Packaging and Handling
Our Phosphate Bonded High Alumina Bricks are handled with care during storage and transportation to maintain their quality and ensure they arrive in optimal condition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What defines a Phosphate Bonded High Alumina Brick?
These bricks are refractory products composed of high alumina content materials, bonded with phosphate to enhance thermal stability, mechanical strength, and resistance to corrosive elements, especially in environments with acidic or mildly basic characteristics.
Q2: Where are Phosphate Bonded High Alumina Bricks typically used?
They are widely used in metallurgical furnaces, cement kilns, waste incinerators, and other high-temperature industrial settings, where their resilience against temperature and chemicals is essential.
Q3: What advantages do phosphate-bonded bricks have over other refractory types?
Phosphate bonding imparts excellent resistance to slag erosion, enhanced mechanical strength, and superior thermal stability. These bricks also offer improved resistance to acidic environments and better thermal shock resistance than many other refractory bricks.
Request a Quote
-
Attachment (Optional)
No file chosen