Aluminum Oxide, Alumina (Al2O3)

Alumina, or aluminum oxide (Al2O3), with its molecular weight of 102, is a foundational element in the realm of technical ceramics, boasting an impressive high melting point of 2,072℃. This makes it the most prevalent ceramic material used across industries, renowned for its role as a traditional yet essential material. The high-purity aluminum oxide version of alumina finds extensive applications in a variety of sectors, credited to its comprehensive utility and adaptability. Its widespread use in technology and industry is attributed to alumina's exceptional properties, including superb electrical insulation, high thermal conductivity, and strong chemical resistance, which collectively make it a versatile and indispensable material.
Moreover, the characteristics of alumina such as good wear resistance and low thermal expansion further enhance its suitability for diverse applications, ensuring components made from alumina can endure extreme conditions and mechanical stress. This positions alumina as a critical resource in applications demanding high durability and reliability. From its insulating properties crucial in electronics to its wear resistance vital in mechanical systems, and thermal conductivity essential for thermal management, alumina's multifaceted performance solidifies its standing as a key material in pushing the boundaries of modern industry and technological innovation.
More Info About Alumina
Products | Structure | Specification | Formulations | Comparison | Applications | Video | FAQs | Brochure
Aluminum Oxide Structure
Alumina, or aluminum oxide (Al2O3), possesses a crystalline structure that significantly contributes to its wide range of impressive properties, making it a staple in the field of technical ceramics. The most common and thermodynamically stable form of alumina under normal conditions is the alpha phase (α-Al2O3), which is characterized by a hexagonal close-packed structure. In this structure, aluminum ions are surrounded by six oxygen ions in an octahedral arrangement, creating a dense and tightly packed lattice that is responsible for alumina's high hardness, melting point, and chemical stability.
The oxygen ions in the alpha-alumina structure form a nearly hexagonal close-packed arrangement, while the aluminum ions fill two-thirds of the octahedral sites within the oxygen lattice. This configuration leads to a high degree of ionic bonding with some covalent character, due to the electronegativity differences between aluminum and oxygen. This bond strength is a key factor behind alumina's excellent mechanical properties, including its resistance to wear and corrosion. Additionally, the stability of the alpha phase contributes to alumina's ability to withstand high temperatures without significant deformation or breakdown, making it an ideal material for high-temperature applications in various industries, from electronics to aerospace.
Read more: Everything You Need to Know about Alumina Ceramics
Aluminum Oxide Specifications
| Material | Alumina | ||||
| Properties | Units | AL997 | AL995 | AL99 | AL95 |
| %Alumina | - | 99.70% | 99.50% | 99.00% | 95.00% |
| Color | - | Ivory | Ivory | Ivory | Ivory & White |
| Permeability | - | Gas-tight | Gas-tight | Gas-tight | Gas-tight |
| Density | g/cm3 | 3.94 | 3.9 | 3.8 | 3.75 |
| Straightness | - | 1‰ | 1‰ | 1‰ | 1‰ |
| Hardness | Mohs Scale | 9 | 9 | 9 | 8.8 |
| Water Absorption | - | ≤0.2 | ≤0.2 | ≤0.2 | ≤0.2 |
| Flexural Strength(Typical 20℃) | Mpa | 375 | 370 | 340 | 304 |
| Compressive Strength (Typical 20℃) |
Mpa | 2300 | 2300 | 2210 | 1910 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (25℃ to 800℃) |
0-6/℃ | 7.6 | 7.6 | 7.6 | 7.6 |
| Dielectric Strength (5mm Thickness) | AC-kv/mm | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Dielectric Loss 25ºC@ 1MHz |
- | < 0.0001 | < 0.0001 | 0.0006 | 0.0004 |
| Dielectric Constant | 25º C@ 1MHz | 9.8 | 9.7 | 9.5 | 9.2 |
| Volume Resistivity (20℃) (300℃) |
Ω·cm³ | >1014 2*1012 |
>1014 2*1012 |
>1014 4*1011 |
>1014 2*1011 |
| Long-term Operating Temperature | ℃ | 1700 | 1650 | 1600 | 1400 |
| Thermal Conductivity (25℃) | W/m·K | 35 | 35 | 34 | 20 |
Aluminum Oxide Formulations
ACM's product formulations are developed to address the varied application problems in which ceramic components are commonly used. Many industrial applications push the envelope on specific requirements leading to the development of new formulations to successfully address them.
| Properties | Unit | Fused Alumina | Reactive Grade Alumina | Ready To Press Alumina (RTP Alumina) | Activated Alumina | |||||||
| Al2O3 Content | % | 95.5 | 99.8 | 98 | 96 | 94 | 92 | 90 | ||||
| Bulk Density | g/cm3 | 3.95 | ~600 | ~1000 | ~600 | ~1100 | ~900 | ~1200 | ~1100 | – | ||
| Grain Size | μm | Customized | Customized | ≈130 | ≈170 | ≈100 | ≈200 | customized | ||||
| Color | – | White | White | White | White | |||||||
| Melting Point | ℃ | 2000 | – | – | – | |||||||
| Hardness | Mohs | 9 | – | – | – | |||||||
| Specific Surface Area | m2/g | – | 0.2-0.5 | 3.5-5 | 2-3 | 6-9 | 6-10 | – | 200-260 | |||
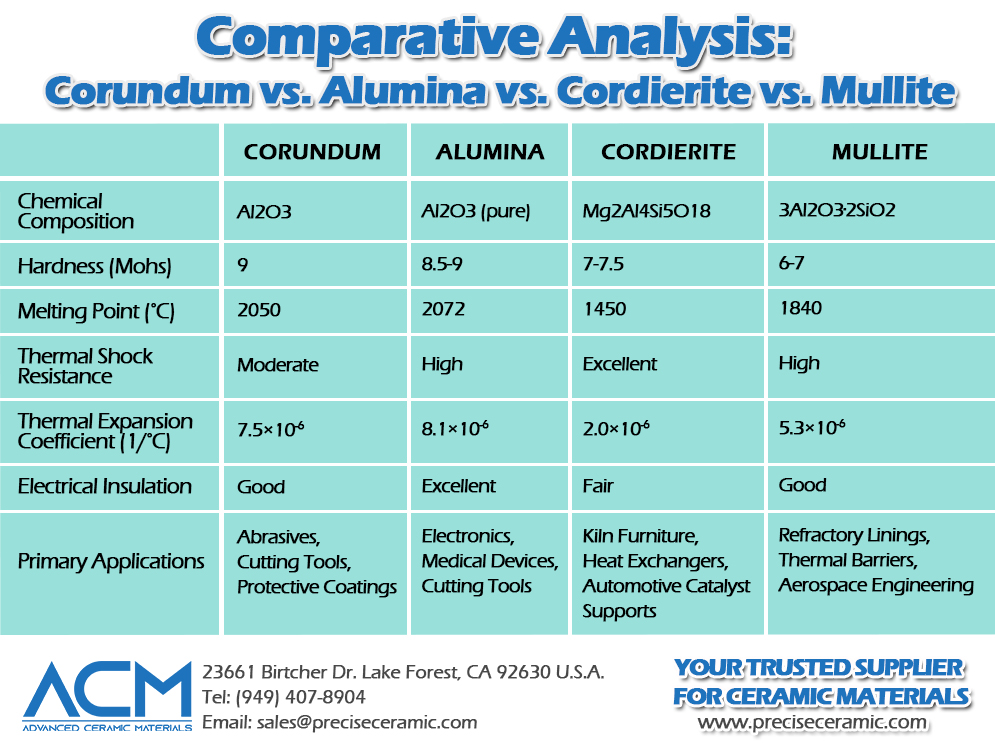
Corundum vs. Alumina vs. Cordierite vs. Mullite
Aluminum Oxide Applications in Various Industries
1. Industrial Appliances
Alumina ceramics are critical in the manufacturing of components for industrial appliances due to their high thermal stability and resistance to wear and corrosion. This includes use in furnaces and as thermal couple protectors, where their ability to withstand extreme temperatures is essential.
2. Coatings
High-purity alumina provides excellent protective coatings for various applications, offering resistance to abrasion, corrosion, and thermal shock. These coatings are particularly valuable in extending the life and performance of equipment in harsh environments.
3. Labware
Alumina's chemical inertness and high melting point make it suitable for labware, such as crucibles and mortars and pestles, used for grinding and heating chemical compounds in laboratories.
4. Engineered Ceramics
Engineered alumina ceramics serve in advanced applications, including CVD processes, ion implants, photolithography, and semiconductor manufacturing, where parts require high purity and precision.
5. Refractories
Alumina's high melting point and resistance to thermal shock make it an ideal material for refractories used in the lining of furnaces, kilns, and reactors in various industrial sectors.
6. Artificial Bones and Joints
Due to its excellent biocompatibility, high strength, and wear resistance, alumina ceramics are used in medical applications to manufacture artificial bones and joints, enhancing the quality of life for patients.
7. Abrasives
The extreme hardness of alumina ceramics makes them perfect for abrasive applications, including grinding media and abrasive tools, where they outperform metals in durability and efficiency.
8. Consumer Electronics
Alumina's electrical insulation properties and thermal management capabilities are leveraged in consumer electronics, providing critical components such as insulators, substrates, and enclosures.
9. Traditional Industry Applications
In traditional industries, alumina ceramics are utilized in products like injector tubes, gas nozzles, and insulators, benefiting from their hardness and thermal resistance.
10. Grinding and Polishing Tools
Alumina's hardness and durability also make it the material of choice for grinding and polishing tools, including mortars and pestles widely used in laboratory settings for preparing samples.
Alumina ceramics stand out for their versatility across a broad spectrum of applications, from high-tech engineering and semiconductor manufacturing to traditional industries and medical prosthetics. Their unique combination of thermal stability, mechanical strength, and chemical inertness allows alumina products to meet the demanding requirements of various fields, driving innovation and enhancing performance in countless applications.
ACM Ceramic Product Categories
Your Aluminum Oxide Ceramics Supplier
Advanced Ceramic Materials (ACM) is a leading supplier of alumina ceramic products of the highest quality for various applications. We are happy to provide advice on materials, design, and application. Feel free to contact us with questions about Al2O3 or other ceramic materials not listed on the website.
| Chemical Formula | Al2O3 |
| Mechanical | |
| Density | 3.9 g/cm3 |
| Hardness | 17.2 GPa |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 380 GPa |
| Flexural Strength | 380 MPa |
| Compressive Strength | 2450 MPa |
| Poisson's Ratio | 0.23 |
| Fracture Toughness | 4 MPa m½ |
| Electrical | |
| Dielectric Strength | 15 ac V/mm |
| Dielectric Constant | 9.9 (@ 1 MHz) |
| Volume Resistivity | 10^14 ohm-cm |
| Thermal | |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | 7.2 x 10^-6/°C |
| Thermal Conductivity | 37 W/(m*K) |
| Specific Heat | 780 J/(Kg*K) |
| Shock Resistance | 250 °C Diff. |
| Maximum Working Temperature | 1700 °C |