Advantages of Using PBN Crucibles in High-Temperature Applications

Pyrolytic Boron Nitride (PBN) crucibles are a great choice for many high-temperature processes. These crucibles offer several benefits, like good heat transfer, high purity, resistance to chemicals, and surfaces that do not stick. Knowing these advantages can help businesses improve their work and get better results.
Good Heat Transfer
PBN crucibles are known for their excellent heat transfer. They have a thermal conductivity of about 60 W/m·K at room temperature, which is higher than many other ceramic materials. This means they heat up quickly and evenly, which is important for processes needing stable temperatures. For example, in crystal growth, even a small temperature change can affect the quality of the final product. PBN crucibles keep the heat even, which leads to better quality.
Their ability to transfer heat well also saves energy. PBN crucibles reach the needed temperature faster and stay there, so they use less energy. This helps lower costs and reduces the impact on the environment.
High Purity
PBN crucibles are made through a process called chemical vapor deposition (CVD). This process makes them very pure, often up to 99.999% (5N). Unlike other crucibles, which might release impurities at high temperatures, PBN crucibles stay pure even under extreme heat. This is very important in industries like semiconductor manufacturing, where even tiny impurities can cause problems.
Because they are so pure, PBN crucibles do not react with the materials inside them. For example, when growing crystals like gallium arsenide (GaAs), PBN crucibles stop any impurities that could cause defects. This helps produce high-quality materials that are reliable and effective.
Resistance to Chemicals
PBN crucibles are also highly resistant to chemicals. They stay stable even in harsh conditions and do not react with most acids, bases, or molten metals. This makes them perfect for processes that involve strong chemicals or very high temperatures.
For example, in metal evaporation, where metals are heated until they turn into vapor, PBN crucibles do not react with the molten metal. They remain stable, even at temperatures over 2,000 degrees Celsius. This reduces the chance of contamination and helps the crucibles last longer, which saves money over time.
Non-Stick Surfaces
PBN crucibles have surfaces that most materials do not stick to. This is useful in processes with molten substances, like metal casting or thin-film deposition. The non-stick surface makes it easy to remove materials and reduces waste.
For example, in Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE), a process used to create thin layers of materials, PBN crucibles prevent the materials from sticking to the crucible walls. This makes it easier to take out the finished product and keeps the materials pure. It also means less cleaning, saving time and effort.
Better Performance in High-Temperature Uses
The mix of good heat transfer, high purity, chemical resistance, and non-stick surfaces makes PBN crucibles ideal for many high-temperature processes. These features help ensure more consistent and reliable results. For example, in semiconductor manufacturing, PBN crucibles help keep materials like silicon pure, leading to better final products.
When making high-purity materials like sapphire or gallium nitride, PBN crucibles provide a clean environment, keep out impurities, and maintain steady temperatures. This results in fewer defects and higher yields, which boosts both efficiency and profits.
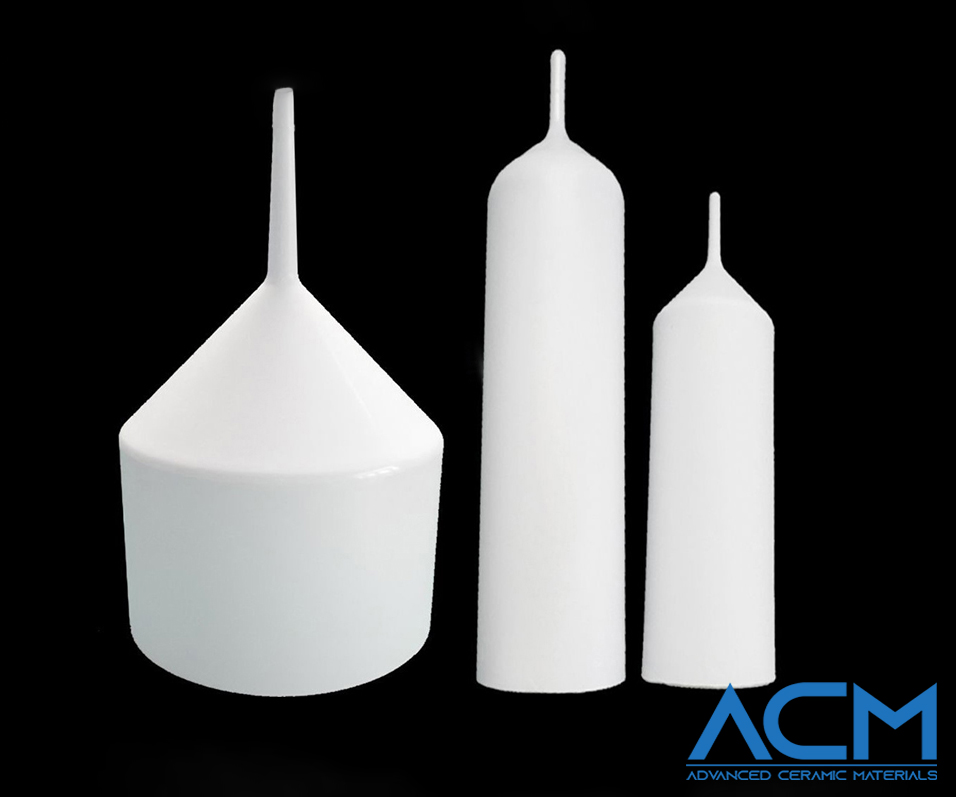
Types of PBN Crucibles for Different Needs
PBN crucibles come in several types, each made for specific uses:
-
MBE Type Crucibles: Used for Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE), these crucibles keep materials pure and ensure accurate material placement. This is key for making high-quality thin films used in semiconductors.
-
LEC Type Crucibles: Made for the Liquid Encapsulated Czochralski (LEC) method, these crucibles help grow high-quality crystals, like gallium arsenide (GaAs), by providing stable and clean conditions.
-
OLED Type Crucibles: Used in making Organic Light Emitting Diodes (OLEDs), these crucibles ensure even thin layers and keep materials pure, which is important for bright, efficient OLED displays.
-
VGF Type Crucibles: Used in the Vertical Gradient Freeze (VGF) method to grow large crystals, like germanium, these crucibles keep temperatures steady, helping to avoid defects and produce high-quality crystals for optics and semiconductors.
Long-Lasting and Cost-Effective
Although PBN crucibles may cost more at first than some other materials, they save money over time. They are strong and last a long time, meaning they do not need to be replaced often. This cuts down on downtime and lowers costs. Their resistance to wear and chemical damage makes them a smart choice for high-temperature uses.
Useful in Many Industries
PBN crucibles are used in many fields, such as electronics, aerospace, and materials science. In electronics, they are important for making semiconductors and LEDs, where purity is key. In aerospace, they are used in processes that involve high-temperature materials, like making superalloys or ceramics. In materials science, PBN crucibles help with experiments that involve high heat, providing a stable environment for research.
They are also great for different types of coating processes, like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). Their stability and non-reactive nature make them an excellent choice for quality results in these processes.
Conclusion
PBN crucibles offer many advantages for high-temperature applications. They transfer heat well, stay pure, resist chemicals, and do not let materials stick. They also come in different types, like MBE, LEC, OLED, and VGF crucibles, to meet the needs of various industries. Advanced Ceramic Materials (ACM) provides high-quality PBN crucibles to help you get the best results in your processes. If you need help choosing the right crucible, contact our experts for guidance.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}
LEAVE A REPLY
SUBSCRIBE OUR NEWSLETTER
- How PBN Crucibles Ensure the Quality of GaN & SiC Epitaxial Materials
- SiC vs. Quartz Focus Rings: A Cost and Performance Analysis for Advanced Etch
- AlN Ceramic Substrates: Enabling Next-Gen Electrostatic Chucks
- The Amor of Semiconductor Tools: Why High-Purity Al2O3 & AlN Are Preferred for Plasma Process Chambers
- Silicon Carbide - Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics for Extreme Environments