Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) - An In-Depth Exploration
1. Introduction
Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) is a monumental advancement in material removal technologies. Renowned for its exceptional hardness and durability, CBN has become indispensable in various industrial applications, particularly those involving ferrous materials. As the second hardest material known to humanity, surpassed only by diamonds, CBN offers unparalleled performance and reliability, making it a cornerstone in modern manufacturing and machining processes.
2. What is Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN)?
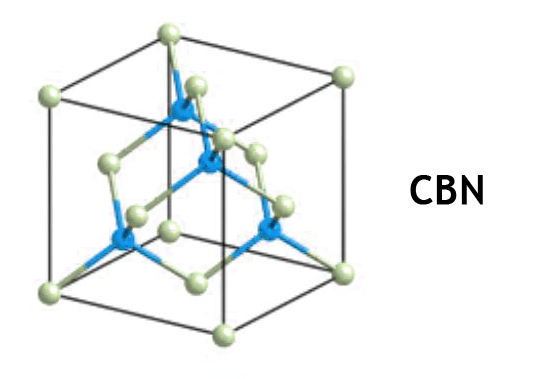
Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) is a synthetic, superhard material with a crystalline structure analogous to that of diamond. Composed of boron and nitrogen atoms arranged in a cubic lattice, CBN exhibits remarkable hardness, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. These properties render it exceptionally suitable for high-precision cutting and grinding applications, especially when working with hard and abrasive materials.
Basic Characteristics
- High Hardness: CBN ranks just below diamond in terms of hardness, making it highly effective for cutting and grinding operations.
- Thermal Stability: Unlike diamond, which can convert to graphite under high temperatures, CBN maintains its structural integrity and hardness.
- Chemical Resistance: CBN is chemically inert, particularly towards ferrous materials, ensuring longevity and performance even in harsh environments.
3. Types of Cubic Boron Nitride
CBN exists in various forms, each tailored to specific applications and performance requirements. The primary types include:
Single Crystal CBN
- Manufacturing Process: Single crystal CBN is synthesized by meticulously controlling hexagonal boron nitride and a catalyst under extreme temperature and pressure conditions.
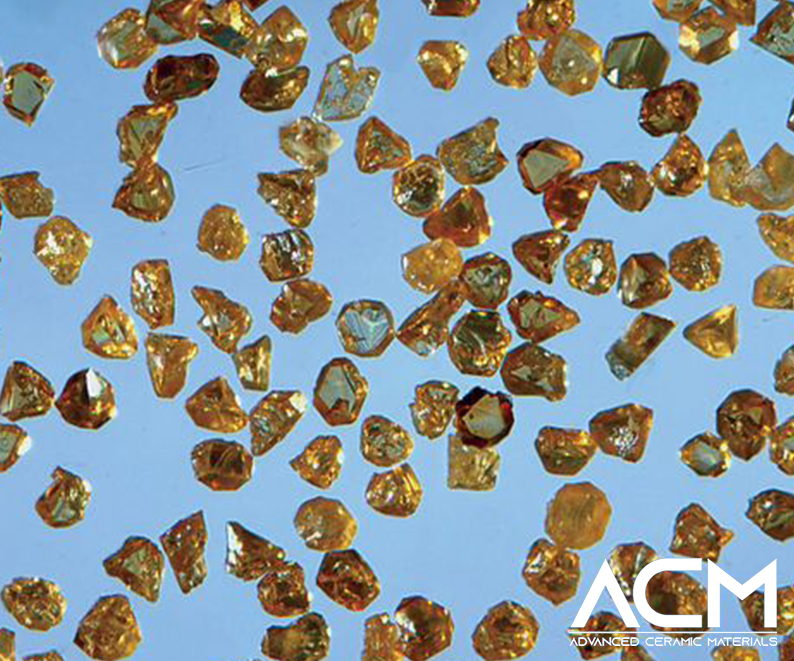
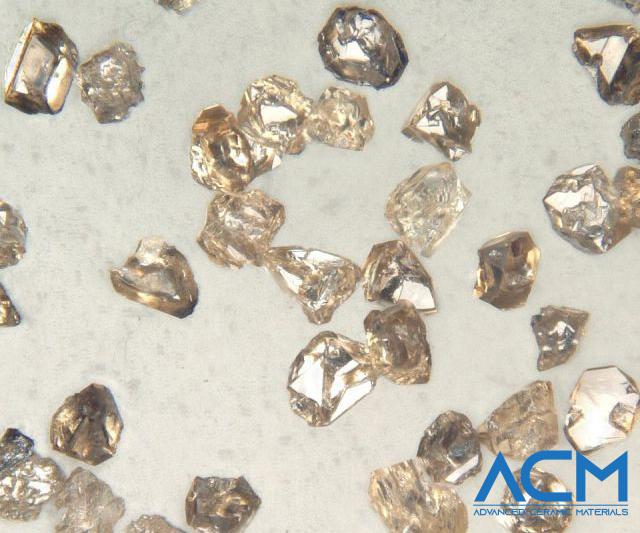
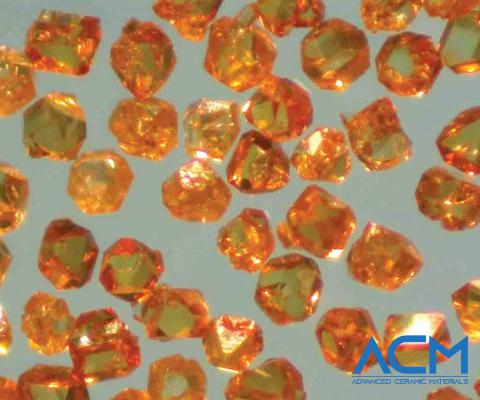
- Characteristics: This form of CBN exhibits diverse crystalline shapes such as truncated tetrahedrons, octahedrons, skew crystals, and twin crystals. Commercially, single crystal CBN particles are typically black, amber, or gold-plated, with particle sizes usually less than 1 mm.
Polycrystalline Cubic Boron Nitride (PCBN)
- Manufacturing Process: PCBN is produced by sintering numerous small CBN grains together, often supported by materials like tungsten carbide (WC), to form a dense, highly durable composite.
- Characteristics: PCBN offers enhanced hardness and wear resistance, making it ideal for high-precision machining and complex component manufacturing.
Other Varieties
In addition to single crystal and polycrystalline forms, CBN is available with various coatings and surface treatments to enhance performance and suitability for specific industrial applications. These specialized treatments can improve properties such as thermal conductivity and surface integrity.
4. Key Properties of Cubic Boron Nitride
CBN's exceptional properties make it a preferred choice for demanding industrial applications. The key properties include:
Structure
CBN boasts a cubic crystalline structure where boron and nitrogen atoms are arranged in a tetrahedral configuration. This arrangement contributes to its outstanding hardness and thermal stability.
Hardness
With a hardness rating second only to diamond, CBN is exceptionally effective in cutting and grinding hard materials. Its superior hardness ensures minimal wear and extended tool life, translating to enhanced productivity and cost-effectiveness in industrial operations.
Thermal Stability
CBN maintains its hardness and structural integrity even at elevated temperatures. Unlike diamond, which can convert to graphite when exposed to high heat, CBN remains stable, making it suitable for high-temperature applications.
Chemical Stability
CBN exhibits high chemical inertness, especially towards iron-based metals. This resistance prevents reactions that could degrade the material or the tool, ensuring consistent performance and longevity.
Thermal Conductivity
CBN has excellent thermal conductivity, which is advantageous in dissipating heat generated during cutting and grinding processes. Efficient heat management reduces thermal stress on tools and workpieces, enhancing precision and reducing the risk of thermal damage.
5. Applications of Cubic Boron Nitride
The unique properties of CBN make it versatile across various industrial sectors. Key applications include:
Abrasives
CBN is widely used as an abrasive for cutting and grinding hard materials, particularly ferrous metals and alloys. Its high hardness and chemical stability ensure efficient material removal with minimal wear.
Read this article if you are interested in abrasive materials.
Cutting Tools
Manufacturers utilize CBN in producing cutting tools designed for high-speed machining of hard materials. These tools offer superior performance, precision, and longevity, making them essential in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and tooling.
Polycrystalline CBN (PCBN) Applications
PCBN is employed in high-precision machining and the production of complex-shaped components. Its ability to maintain shape and sharpness under extreme conditions makes it ideal for intricate manufacturing processes.
Other Industrial Applications
Beyond cutting and grinding, CBN is used in environments that demand high wear resistance, thermal conductivity, and stability. Applications include components and tools exposed to harsh conditions, such as high-temperature furnaces, abrasive environments, and precision instrumentation.
6. Why is Cubic Boron Nitride Called a Superhard Material?
Synthesis Process
CBN is synthesized by transforming hexagonal boron nitride in the presence of a catalyst under extreme conditions—pressures ranging from 3,000 to 8,000 MPa and temperatures between 800°C to 1,900°C. The choice of catalyst materials, typically alkali metals, alkali earth metals, tin, lead, antimony, and their nitrides, plays a crucial role in achieving the desired cubic structure.
Hardness and Wear Resistance
CBN's hardness is a direct result of its strong covalent bonding and cubic crystal structure. This intrinsic hardness makes CBN the second hardest material after diamond. Additionally, CBN's exceptional wear resistance prolongs the lifespan of cutting and grinding tools, reducing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance.
7. Conclusion
Cubic Boron Nitride's unparalleled hardness, thermal stability, and chemical resistance make it an invaluable material in various industrial applications. Its ability to perform consistently under extreme conditions ensures its continued relevance and indispensability in modern manufacturing and machining processes.
Acknowledgments
Thank you for engaging with this exploration of Cubic Boron Nitride. At Advanced Ceramic Materials (ACM), we are committed to providing innovative ceramic solutions that drive industrial excellence. Should you have any inquiries or need personalized assistance, our dedicated team is here to support your endeavors.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}
LEAVE A REPLY
SUBSCRIBE OUR NEWSLETTER
- How PBN Crucibles Ensure the Quality of GaN & SiC Epitaxial Materials
- SiC vs. Quartz Focus Rings: A Cost and Performance Analysis for Advanced Etch
- AlN Ceramic Substrates: Enabling Next-Gen Electrostatic Chucks
- The Amor of Semiconductor Tools: Why High-Purity Al2O3 & AlN Are Preferred for Plasma Process Chambers
- Silicon Carbide - Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics for Extreme Environments