Different Ceramic Bearing Ball Grades and How to Choose

Ceramic bearing balls have become indispensable in various high-performance applications due to their superior properties compared to traditional steel bearings. They offer excellent resistance to wear, corrosion, and high temperatures, making them ideal for demanding environments. However, choosing the right grade of ceramic bearing balls is crucial to ensuring optimal performance and longevity. This article compares the different grades of ceramic bearing balls and guides you in selecting the appropriate grade for your application.
Understanding Ceramic Bearing Ball Grades
Ceramic bearing balls are graded based on several parameters, including sphericity, surface finish, and size variation. These grades are standardized internationally, ensuring consistency and reliability across different manufacturers and applications.
Key Parameters for Grading:
- Sphericity: The degree to which the ball is perfectly spherical. Higher grades have tighter tolerances for sphericity.
- Surface Finish: The smoothness of the ball's surface, which impacts friction and wear.
- Size Variation: The permissible deviation in the ball's diameter, with higher grades having more stringent size tolerances.
Common Ceramic Materials for Bearing Balls:
-
- Known for its high strength, fracture toughness, and resistance to wear and high temperatures.
- Frequently used in aerospace, automotive, and high-speed machinery applications.
2. Zirconia (ZrO₂):
-
- Offers high strength, excellent toughness, and resistance to wear and corrosion.
- Ideal for applications in medical devices, pumps, and chemical processing equipment.
3. Alumina (Al₂O₃):
-
- Provides good mechanical strength, hardness, and thermal stability.
- Commonly used in industrial and electrical applications due to its insulating properties.
-
- Extremely hard and resistant to wear, chemical corrosion, and high temperatures.
- Used in applications requiring high endurance and exposure to harsh environments.
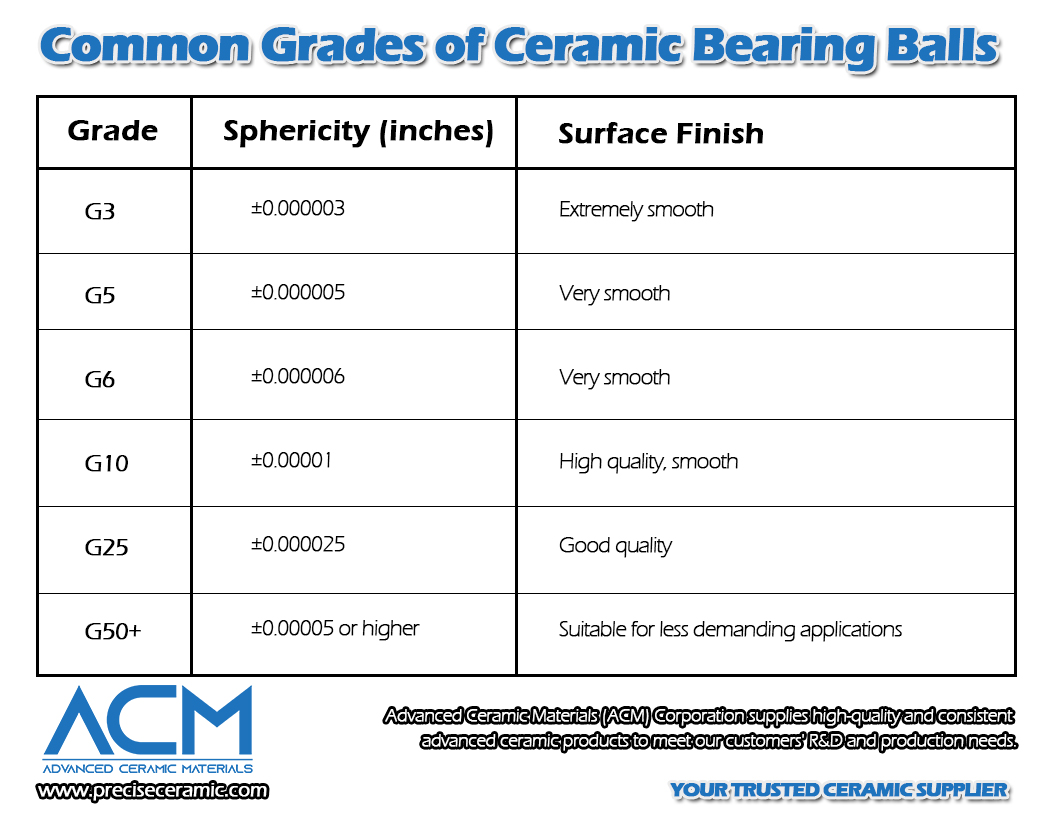
Common Grades of Ceramic Bearing Balls
-
Grade 3 (G3)
- Sphericity: ±0.000003 inches
- Surface Finish: Extremely smooth
- Applications: Aerospace, medical devices, and other high-precision equipment requiring exceptional accuracy and performance.
-
Grade 5 (G5)
- Sphericity: ±0.000005 inches
- Surface Finish: Very smooth
- Applications: High-end ball bearings, and precision instruments where high performance is critical.
-
Grade 6 (G6)
- Sphericity: ±0.000006 inches
- Surface Finish: Very smooth, even higher precision than G10
- Applications: Ultra-precision instruments, specialized high-performance bearings.
-
Grade 10 (G10)
- Sphericity: ±0.00001 inches
- Surface Finish: High quality, smooth
- Applications: High-precision instruments, and high-performance bearings that require reliable performance.
-
Grade 25 (G25)
- Sphericity: ±0.000025 inches
- Surface Finish: Good quality for general precision applications
- Applications: Standard precision ball bearings are used in various industrial applications.
-
Grade 50 and Above (G50+)
- Sphericity: ±0.00005 inches or higher
- Surface Finish: Suitable for less demanding applications
- Applications: General-purpose bearings where ultra-high precision is not necessary.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Grade
When selecting the appropriate grade of ceramic bearing balls for your application, consider the following factors:
-
Application Requirements
- Determine the level of precision needed. High-precision applications like aerospace and medical devices often require grades G3 to G10.
- For general industrial applications, grades G25 to G50 may suffice.
-
Load and Speed
- Higher grades (G3, G5) are better suited for applications involving high loads and speeds due to their superior sphericity and surface finish.
-
Operating Environment
- Consider the environmental conditions, such as temperature, corrosion, and exposure to chemicals. Ceramic materials like silicon nitride (Si₃N₄) and zirconia (ZrO₂) offer excellent resistance to harsh environments.
-
Cost vs. Performance
- Higher-grade balls typically come at a higher cost. Balance the cost against the performance benefits to determine the most economical choice for your needs.
Conclusion
Choosing the right grade of ceramic bearing balls is critical to achieving the desired performance and longevity in your application. By understanding the different grades and considering factors like application requirements, load and speed, operating environment, and cost, you can make an informed decision. Whether you need ultra-high precision for aerospace applications or general-purpose bearings for industrial use, there's a suitable ceramic bearing ball grade to meet your needs.
For further assistance or to explore our range of ceramic bearing balls, including various grades, please visit Advanced Ceramic Materials (ACM) or contact our experts for personalized guidance.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}
LEAVE A REPLY
SUBSCRIBE OUR NEWSLETTER
- How PBN Crucibles Ensure the Quality of GaN & SiC Epitaxial Materials
- SiC vs. Quartz Focus Rings: A Cost and Performance Analysis for Advanced Etch
- AlN Ceramic Substrates: Enabling Next-Gen Electrostatic Chucks
- The Amor of Semiconductor Tools: Why High-Purity Al2O3 & AlN Are Preferred for Plasma Process Chambers
- Silicon Carbide - Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics for Extreme Environments