How to Choose the Right PBN Crucible Type for Your Application
PBN crucibles are essential in high-temperature and vacuum applications. They are widely used in industries like semiconductor manufacturing, crystal growth, and OLED production. Choosing the right crucible shape and type is crucial for achieving optimal results. This guide will help you understand the different shapes and types of PBN crucibles available. It will enable you to make an informed decision based on your specific needs.
Understanding Crucibles
What is PBN?
Pyrolytic Boron Nitride (PBN) is a high-performance ceramic material. It is known for its thermal stability and chemical resistance. PBN is made through a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process. This process results in a pure, dense, and strong material. PBN’s non-reactive nature makes it ideal for high-purity environments, like semiconductor manufacturing. It withstands extreme temperatures and resists contamination, making it a preferred choice in various high-tech industries.
Why Choose PBN Crucibles?
PBN crucibles offer many advantages. They don’t contaminate the materials they hold, which is crucial in processes where even small impurities can impact quality. PBN crucibles also have excellent thermal shock resistance. They can endure rapid temperature changes without cracking. This durability makes them reliable for repeated use in demanding environments. Additionally, PBN crucibles are electrically insulating, making them suitable for processes where electrical conductivity must be avoided.
Common Shapes of Crucibles
Crucibles come in various shapes, each designed for specific applications. Understanding these shapes will help you choose the right one for your process.
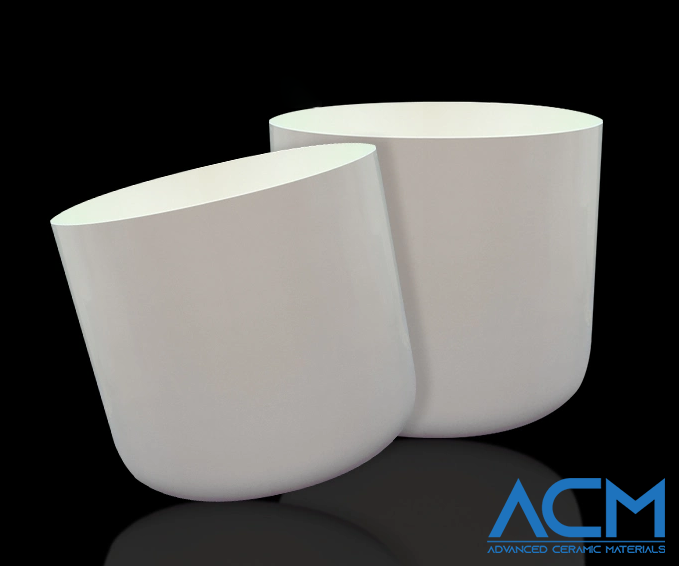
Cylindrical Crucibles
Cylindrical crucibles are often used when uniform heating is required. Their round shape ensures even heat distribution across the material. This consistent heating is vital in processes like crystal growth, where temperature uniformity influences crystal quality. Cylindrical crucibles are available in various sizes. They are versatile and suitable for many applications, making them popular in different industries.
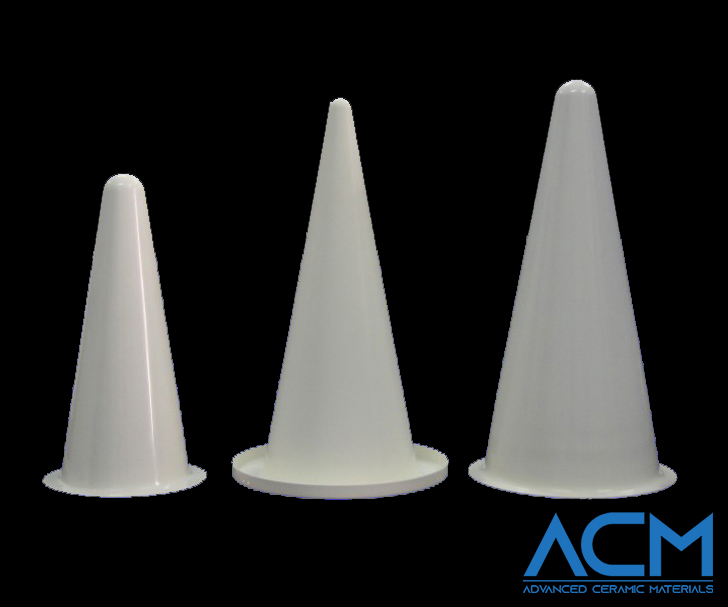
Conical Crucibles
Conical crucibles have a tapered design that makes pouring and collecting materials easier. The shape allows molten materials to flow smoothly without spilling. Conical crucibles are especially useful in metal evaporation processes. In these processes, precise material transfer is essential to avoid waste and ensure consistency. The narrow bottom of the conical crucible also helps concentrate heat, making it efficient for processes needing localized heating.
Boat Crucibles
Boat crucibles are shaped like small boats and are used in horizontal heating setups. Their elongated design allows for even spreading of materials. This feature is beneficial in thin-film deposition processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). Boat crucibles are easy to load and unload. This convenience is important in processes that involve repeated applications of thin layers. The design also reduces the risk of material overflow during heating.
Rectangular Crucibles
Rectangular crucibles provide a flat surface, ideal for spreading materials uniformly. This shape is commonly used in chemical reactions where even heating is required. Rectangular crucibles are also suitable for processes where the material needs to stay in place, such as in solid-state reactions. The flat surface ensures consistent contact with the heating source, leading to uniform temperature distribution.
Specific Types of PBN Crucibles and Their Applications
Beyond general shapes, specific types of PBN crucibles are designed for particular processes. Understanding these types helps you choose the right crucible for specialized applications.
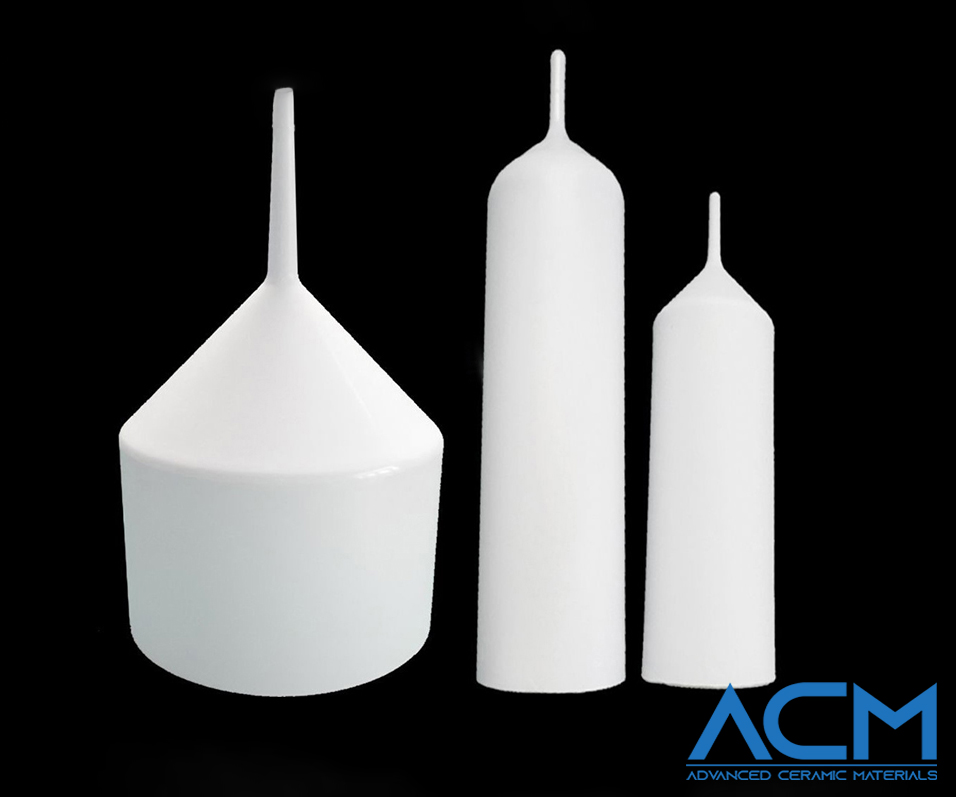
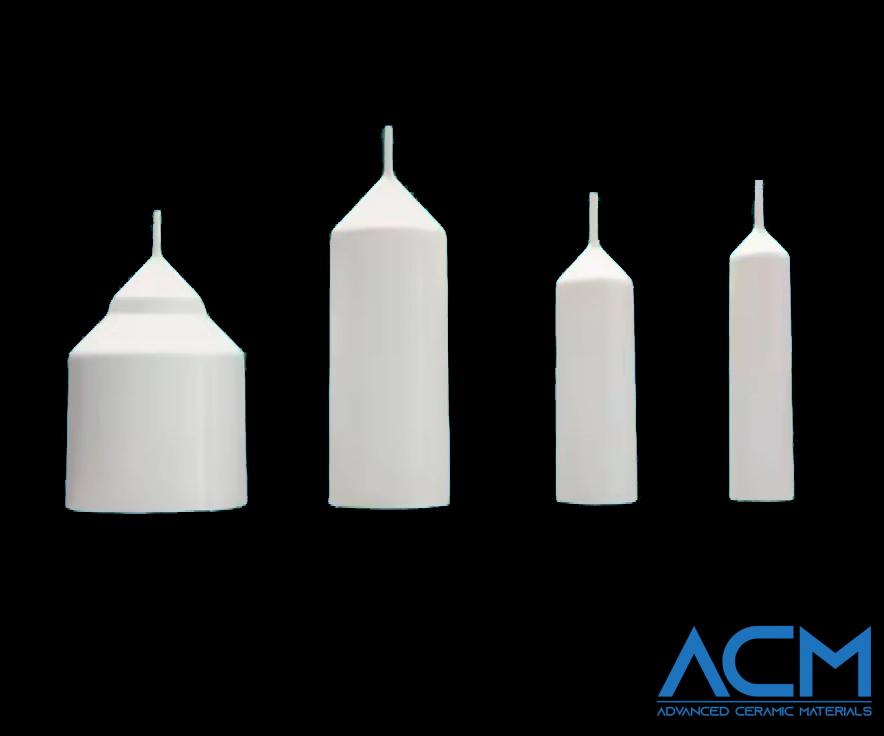
MBE Type Crucible
Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE) is a precise technique used to deposit thin films of materials onto substrates. MBE Type PBN crucibles are designed for this process. They ensure high-purity and high-precision material deposition. These crucibles are crucial in semiconductor manufacturing. In these processes, thin layers of materials like gallium arsenide (GaAs) are deposited to create electronic components. MBE crucibles minimize contamination and ensure consistent deposition, which is vital for producing high-quality semiconductors.
LEC Type Crucible
The Liquid Encapsulated Czochralski (LEC) method grows high-quality single crystals like GaAs, which are vital in the semiconductor industry. LEC Type PBN crucibles are built to handle the tough conditions of this process. They hold the molten material from which the crystal is drawn. The crucible's purity and stability are crucial because contamination can harm the crystal's quality. LEC crucibles ensure smooth crystal growth, leading to high-quality crystals with minimal defects.
OLED Type Crucible
Organic Light Emitting Diode (OLED) fabrication requires precise control over the materials and processes used. OLED Type PBN crucibles are tailored for this purpose. They ensure that the materials used in OLED production are handled with the highest purity. These crucibles are designed to withstand the specific conditions of OLED production, such as high temperatures and reactive environments. Using these specialized crucibles helps achieve uniform thin-film deposition, which is critical for the performance of OLED displays.
VGF Type Crucible
The Vertical Gradient Freeze (VGF) method is used to grow large single crystals, such as germanium, which are used in infrared optics and semiconductor applications. VGF Type PBN crucibles are designed to hold the material during the crystal growth process. The design ensures uniform temperature distribution. This uniformity is essential for producing large, defect-free crystals. The high purity of PBN crucibles prevents contamination, ensuring that the crystals meet the strict quality standards required for high-tech applications.
Choosing the Right PBN Crucible for Your Application
Selecting the right crucible involves understanding your specific process requirements. Here’s how you can make the best choice:
1. Evaluate Your Needs
Start by considering the materials you will be working with and the temperatures involved. Determine whether you need uniform heating, efficient pouring, or precise material deposition. For example, if your process requires even heating, a cylindrical crucible might be the best choice. If you need to pour molten material, a conical crucible could be ideal.
2. Match the Shape and Type to Your Application
Choose a crucible shape that aligns with your process. For example, use boat or rectangular crucibles in horizontal processes. For specialized processes like MBE, LEC, OLED, or VGF, select the corresponding crucible type. Each shape and type of crucible is designed to optimize specific aspects of these processes. These aspects include improving material flow, enhancing heat distribution, or ensuring purity.
3. Consider Size and Capacity
Ensure that the crucible’s size and shape can hold the required material for your process. The crucible should also fit within your equipment without any issues. Consider the scale of your operation—whether it’s a small batch or large-scale production—and choose a crucible that matches your needs.
Conclusion
Choosing the right PBN crucible shape and type is key to your application’s success. You can achieve optimal performance by understanding your process needs and selecting the appropriate crucible. Whether you need uniform heating, efficient pouring, or precise material handling, the right crucible can greatly impact your results. If you’re unsure which crucible to choose, contact our experts for advice.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}
LEAVE A REPLY
SUBSCRIBE OUR NEWSLETTER
- How PBN Crucibles Ensure the Quality of GaN & SiC Epitaxial Materials
- SiC vs. Quartz Focus Rings: A Cost and Performance Analysis for Advanced Etch
- AlN Ceramic Substrates: Enabling Next-Gen Electrostatic Chucks
- The Amor of Semiconductor Tools: Why High-Purity Al2O3 & AlN Are Preferred for Plasma Process Chambers
- Silicon Carbide - Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics for Extreme Environments