What You Need to Know About Zirconia Implants
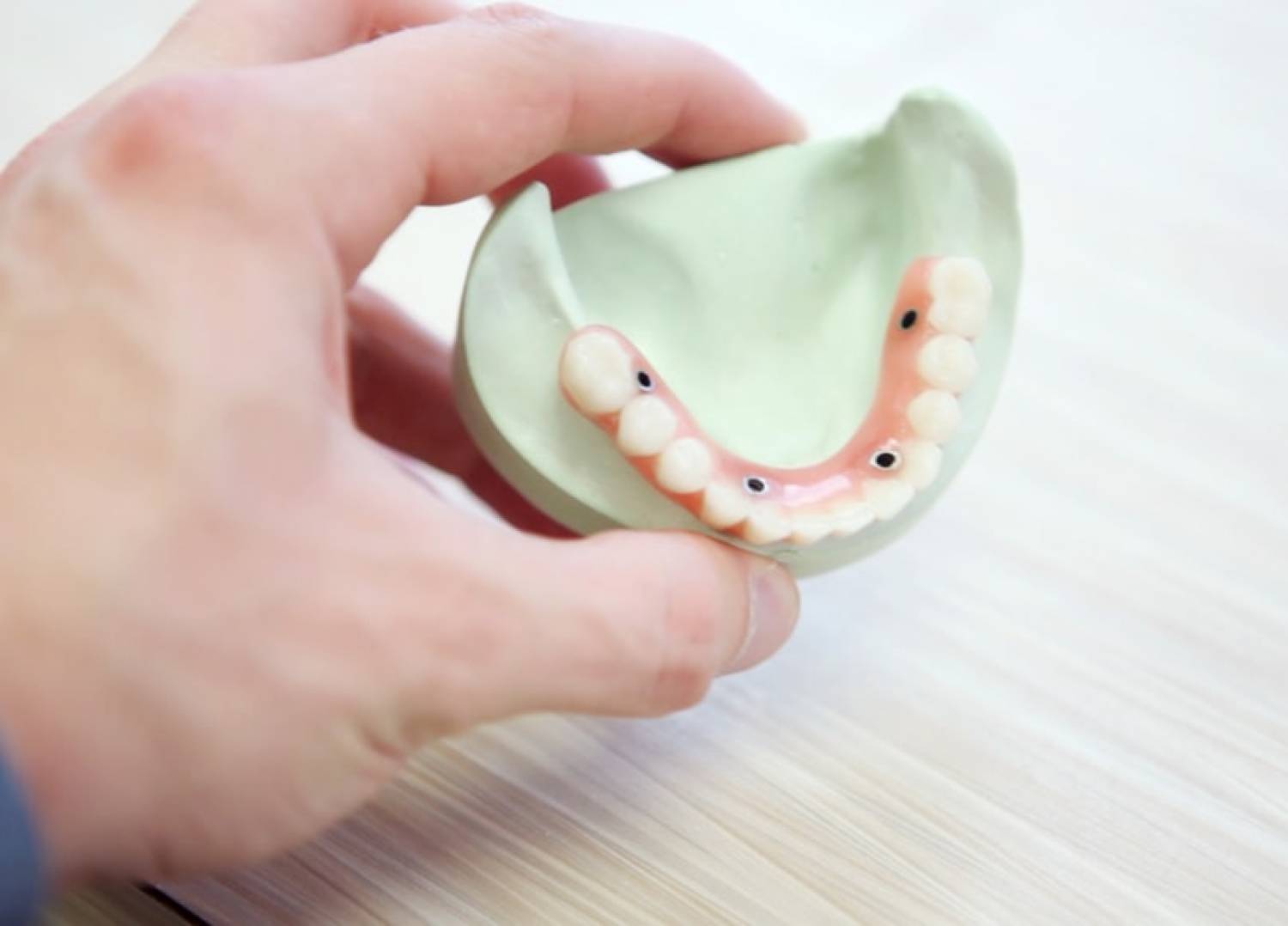

The ceramic material zirconia (also known as zirconium dioxide, ZrO2) is an important synthetic material used in many productive ways today. It is obtained from zircon sand. Zirconia ceramic is obtained when zirconium undergoes oxidation to produce zirconia dioxide (ZrO2). Recently, zirconia implants have become a popular topic, mainly because of their bioinert nature and durability. It combines the strength of the zirconium metal and the heat-resistant ability of the ceramic to provide the properties desired in dental implants. In this article, you'll learn more about the uses of zirconia in implants.
Zirconia Implants: What Are They?
Zirconia implants are the non-metal alternatives to titanium implants. If you've had issues with metal implants before, you might want to check out zirconia implants. They consist of zirconia metal and oxygen. With dental implants becoming widely available, it might help you to know the options available in case you need one tomorrow. Zirconia is an ideal dental implant for some valuable reasons. Zirconia implants are biologically inactive, to begin with. This means that they do not react with any biological material, nor will they decay in your mouth. Zirconia dental implants are strong and long-lasting, which can be traced to the zirconium content. Besides, zirconium dioxide, the ceramic form of the transition metal, is a very strong material.
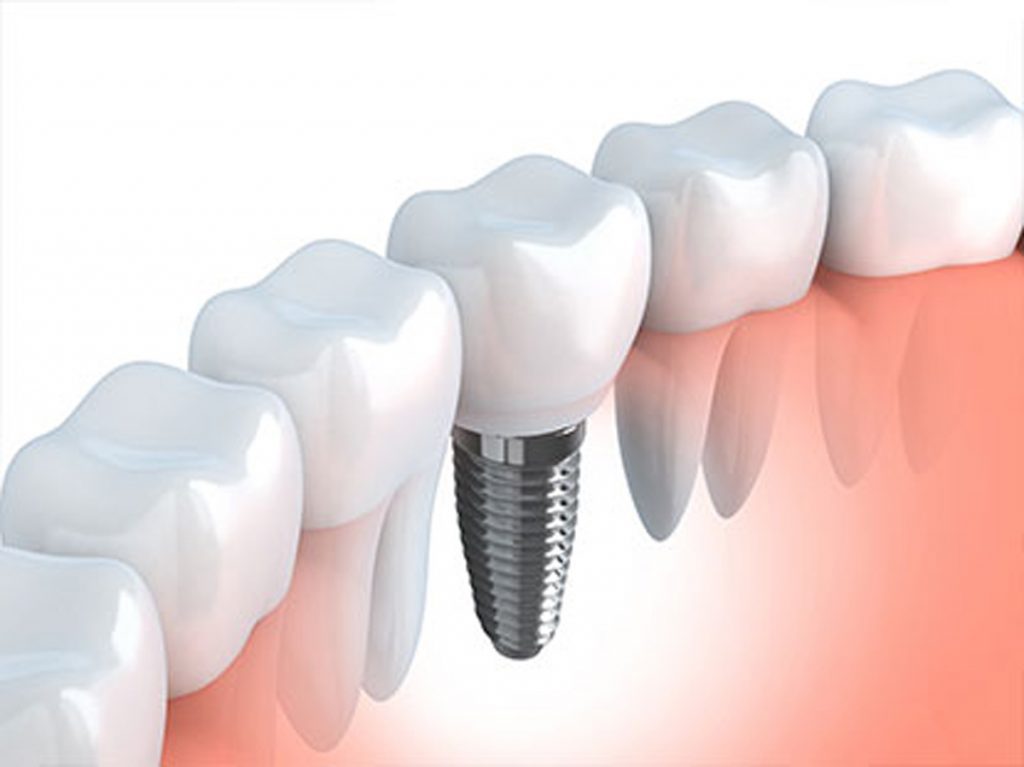
Aside from being compatible with human tissues, Zirconia implants have low bacterial attraction, meaning that they hardly attract the actions of bacteria on the synthetic tooth, and they hold up against wear, fracture, and corrosion relatively well. Finally, they're an ideal implant in humans because you can easily change the color of the material to match that of the patient's natural tooth. This ensures the natural color of the teeth is preserved even in the synthetic implants.
Types of Zirconia Implants
The main types of Zirconia dental implants are one-piece and 2-piece ceramic implants. Other types of zirconia implants containing ceramic that are used in dental implants are:
- Yttrium cation-doped tetragonal zirconia polycrystals
- Zirconia toughened alumina
- Magnesium cation-doped partially stabilized zirconia
Advantages of Zirconia Implants
1. They're hypoallergenic
Since zirconia implants are biologically inactive, they make a perfect alternative for people allergic to metals like titanium. Observations over time have even shown that you could, in addition to the irritation, lose your implants after the surgery. Zirconia implants, on the other hand, are safe and do not cause any irritation.
2. Integrated well with the bone and gum tissues
Zirconia implants fit well into the bone, and the soft tissues surrounding the teeth are pretty accommodating. If the implant fails to bond with the bone, that could be the end of the surgery. With zirconia, this is not an issue because it has a long history of blending in very well.
3. No metallic taste
Unlike metallic implants, zirconia dental implants do not dissolve in the mouth or give any taste. They are inert and neutral in taste.
4. Heals faster
Since zirconia isn't metal, it does not conduct heat and will allow your gum to heal faster if need be.
5. They are very strong
Due to the resilience and strength of zirconia implants, they tend to last longer and can hold the weight of your jaws, especially when eating. This is a desirable quality in any dental implant because if it doesn't hold well under the weight of your jaws, it could lead to complications.
6. They're corrosion-resistant
These implants are typically hard and resistant to corrosion. Zirconia is resistant to corrosion by chemical and conduction of electricity and heat. This is unlike titanium which will likely corrode in the wet environments of the mouth, especially in the presence of other metals.
7. Zirconia does not conduct electricity
Zirconia does not conduct electricity, which is a big plus. It discourages the growth of bacterial growth on the surface of the implant. This helps in creating a healthier oral environment.
8. Accumulation of plaque
When it comes to the buildup of plaque on the teeth, they'll have a hard time attaching or adhering to the zirconia implants, thereby helping to maintain the best oral hygiene.
Disadvantages of Zirconia Implants
While zirconia implants do sound like magic, they're not without faults. To help you make informed decisions about your dental health, here are the downsides of zirconia dental implants:
- Limited specialization on zirconia implants. Not many dentists in the states are familiar with zirconia. The most popular option is still titanium implants.
- It is mainly a one-piece cement-retained system, which is not as flexible as is desired
- It is not as affordable as the titanium implant option. This is mainly because it is still a new solution in the market.
Zirconia vs Titanium Implants: Which Is Better?
Since the 1960s, titanium implants have been the predominant choice for dental implants. Implantation generally has a 90+ success rate. Zirconia is not as popular yet, so not much is known about applying it in the U.S. While zirconia implants are a bit more innovative, the choice of which to use ultimately rests on the patient's regarding the best solution for their situation.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}
LEAVE A REPLY
SUBSCRIBE OUR NEWSLETTER
- How PBN Crucibles Ensure the Quality of GaN & SiC Epitaxial Materials
- SiC vs. Quartz Focus Rings: A Cost and Performance Analysis for Advanced Etch
- AlN Ceramic Substrates: Enabling Next-Gen Electrostatic Chucks
- The Amor of Semiconductor Tools: Why High-Purity Al2O3 & AlN Are Preferred for Plasma Process Chambers
- Silicon Carbide - Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics for Extreme Environments