The Use of Rare Earths in Functional Ceramics

Rare Earths & Functional Ceramic
Rare Earth Elements consist of 17 metal elements, including 15 lanthanides, scandium, and yttrium. In the recent 20 years, rare earth elements have made great contributions to the development of high-tech industries. For example, they have been applied in functional ceramics.
Functional ceramic is a new type of ceramic material for meeting the developing needs of computer science, automatic control, sensing technology, bioengineering, environmental science, and other fields. It can realize certain functions with direct effects and coupling effects of electricity, magnetism, sound, light, heat, and power. Because of its numerous types and various functions, functional ceramic has been widely used in electrical equipment, signal processing, sensor measurement, semiconductor devices, superconducting materials, and other areas.
Functional ceramic is closely related to rare earth. It is known that most superconducting ceramics contain rare earth elements. For example, yttrium barium copper oxide (YBCO) is a kind of oxide ceramic with excellent high-temperature superconductivity. With the addition of rare earth in the raw materials, the agglutinating property, density, intensity and other unique functions of functional ceramics will be greatly improved.
Applications of Rare Earth in Functional Ceramics
Rare earth for superconducting ceramics
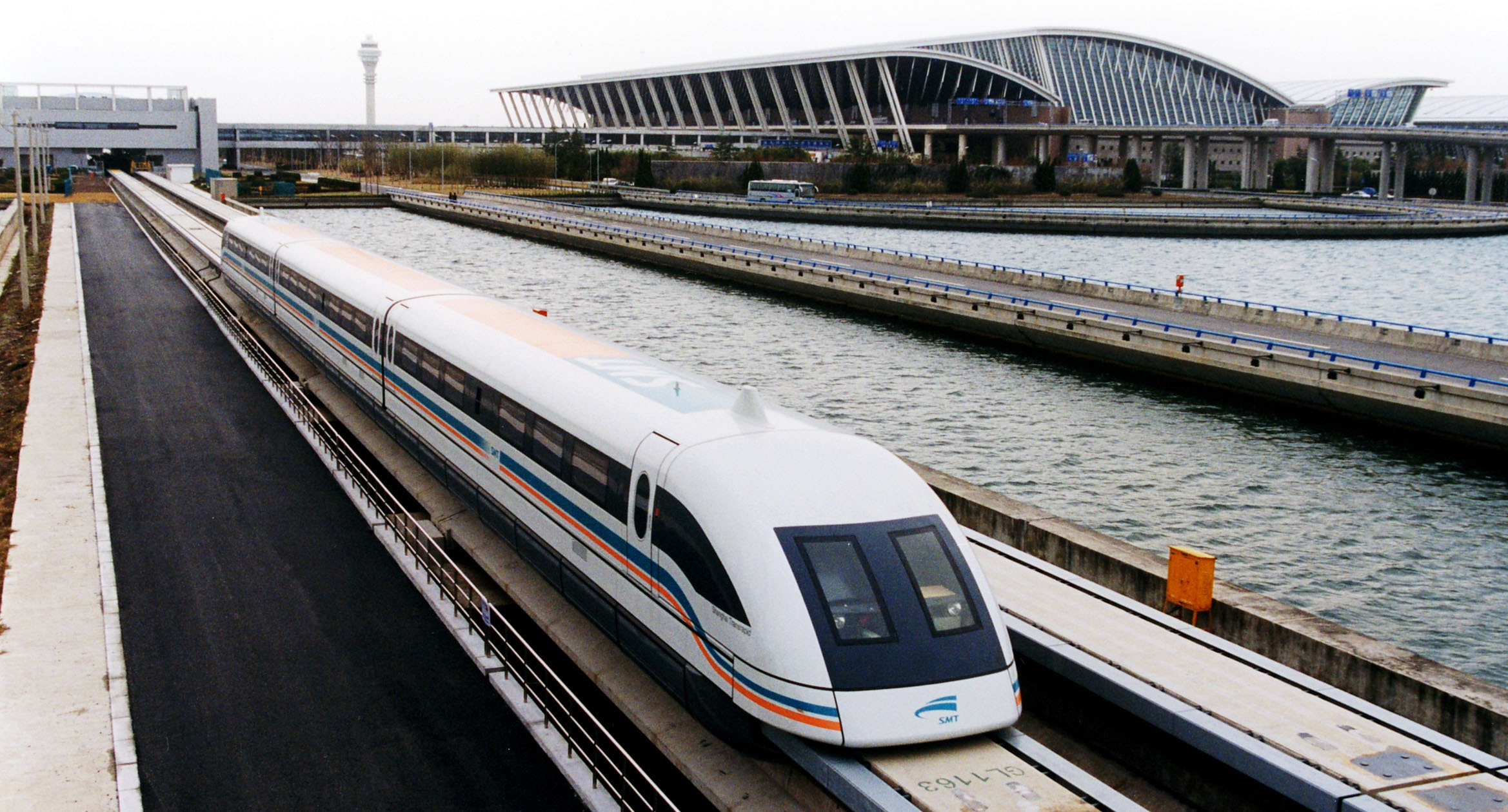
Scientists have been studying the functions and applications of high-temperature superconducting ceramics with rare earth since 1987. According to the Japanese scientists’ research, by replacing y in YbCo with Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd and other light rare earths, the critical magnetic field strength and flux pinning force of InBCo will be remarkably improved. With special processing, the InBCo block can capture more than 10t magnetic field at 77k, which can substitute for the magnet of the maglev train.

Peking University did related research, in which yttrium, barium oxide and copper stratified evaporation were diffused with a supporting base of ZrO2 under a high temperature of 392℉. After heat processing with a temperature between 1472℉ to 1652℉, superconducting ceramics will have an excellent temperature coefficient of metallic resistance. Japan Kagoshima University found that adding rare earth lanthanum into Strontium oxide and Niobium oxide can produce a special ceramic film that has superconductivity quality at 255k.
Rare Earth for Piezoceramic
Lead titanate (PbTiO3) is a typical piezoelectric ceramic with mechanical energy-electric coupling effects. It can be applied in high temperature and high-frequency conditions since it has a high Curie temperature (914℉) and low dielectric constant. However, this material is likely to have microcracks because of the cubic/ tetragonal phase transition during the cooling process. With the addition of rare earth, PbTiO3 can turn into re-PbTiO3 with better microstructure and higher density. The study has found that the dielectric constant of re-PbTiO3 ceramics will reduce and piezoelectric anisotropy will increase due to the substitution of rare earth ions re3+. This material can be used in the manufacture of ultrasonic transducers of high sensitivity and resolution because ceramic’s dielectric constant and radial electromechanical coupling coefficient decrease and high-frequency resonance peak become simple.
By adding rare earth oxides such as La2O3, Sm2O3, and Nd2O3 into the piezoelectric ceramics, its sintering performance can strongly be improved and its electrical properties and piezoelectric properties will be more stable. The quality of PZT ceramics can be improved by adding 0.2%-0.5% rare earth oxide CeO2. Ceramics’ volume resistivity will increase, which is good for achieving high temperature and high electric field polarization. Besides, the aging resistance of the ceramics will also be improved. PZT ceramics modified by rare earth have been widely used in high-voltage generators, ultrasonic generators, underwater acoustic transducers, and other devices.
Rare Earth for Conductive Ceramic
The yttrium-stabilized zirconia ceramic with the addition of rare earth oxide Y2O3 has good thermal stability and chemical stability at high temperatures. As a good oxygen ion conductor, this ceramic plays an important role in ion-conductive ceramics. YSZ ceramic sensor has been used to measure the oxygen partial pressure in the automobile exhaust gas. Besides, it can effectively control air and fuel ratio which can remarkably save energy. Now it has been widely applied in industrial boilers, smelting furnaces, incinerators and other combustion-based equipment. Precise ceramics with rare earth can also be used as SOFC battery bipolar plates, porous cathode, and Porous anode material.

Rare Earth for Dielectric Ceramic
Dielectric ceramics are mainly used for ceramic capacitors and microwave dielectric elements. With the addition of La, Nd, Dy and other rare earth elements, the dielectric properties of the TiO2、MgTiO3、BaTiO3 will be remarkably improved. In the dielectric ceramic for thermal compensation capacitors, rare earth can be added to realize the improvement or adjustment of the dielectric constant, temperature coefficient, and quality factor of the ceramic, and expand its application range. Microwave dielectric ceramic has a large category. The ceramic mixed with rare earth oxide BaO-Re2O3-TiO2 is a common material with various applications with the dielectric constant ε over 80.
Rare Earth for Sensitive Ceramic
Sensitive ceramic is one of the key functional ceramics, with the characteristic that it has sensitive reactions towards some external conditions such as voltage, gas composition, temperature, humidity and so on. It is also known as the sensor ceramic widely used in sensing elements because it can control the circuit or monitor the environment. There is a close relationship between rare earth and the properties of sensitive ceramics.
- Electro-Optical Ceramic
Transparent PLZT ceramic can be made when La2O3 is added to PZT. PLZT electro-optical ceramics has an electro-optical effect, secondary electro-optic effect (Kerr effect), light scattering effect, and optical memory effect. Among them, the Kerr effect is most commonly being used, such as shielding goggles for nuclear explosive radiation, windows for heavy bombers, optical communication modulators, holographic recording devices, etc. As PLZT electro-optical ceramic can change its optical properties with the use of the electric field, it marks that ceramic material can be applied in the field of functional optics.
- Pressure Sensitive Ceramic
According to the study on the effect of rare earth elements on the electrical properties of ZnO pressure-sensitive ceramics, the varistor voltage vlma value was significantly improved after adding rare earth oxide la2o3 into the ceramic. When the addition increases from 0.1% to 10%, the non-linear coefficient α of the ceramic will decrease from 20 to 1, at which the ceramic is basically non-pressure sensitive. Therefore, low concentrations of rare earth elements can increase the value of ZnO ceramic’s varistor voltage. However, a high concentration of rare earth elements will make the ceramic with pressure sensitive characteristics.
- Gas Sensitive Ceramic
The Dalian University of Technology has studied the function of ReFeO3 material with the addition of rare earth oxide Re2O3. According to their findings, ultrafine gratification of materials is an important factor to improve the sensitivity of the gas sensor. Besides, different kinds of rare earth have different impacts on the microstructures of the materials. It was found that the ReFeO3 series had higher sensitivity to ethanol and the order of sensitivity was ndfeo3> smfeo3> lafeo3. Besides, they have low sensitivity to gasoline and little reaction to other gases, therefore they have wide options.
- Thermal Ceramic
Currently, barium titanate (BaTiO3) is the most frequently studied and widely used thermal ceramic. When the batio3 is mixed with rare earth elements such as la, ce, sm, dy, y, the resistivity of the ceramic is significantly reduced. Because Re3+ replaces part of Ba2+, leading to the excess positive charge and forming weakly bound electrons with the effect of Ti4+. However, when the addition of rare earth exceeds a certain value (for example, Moles of La> 0.35%), the resistivity of the ceramic increases abruptly, and the ceramic can even become an insulator.
- Humidity Sensitive Ceramic
There is a wide variety of wet-sensitive ceramics. Their main additions of rare earth are lanthanum and its oxides, such as Sr1-xlaxSnO3, La2O3-TiO2, and La2O3-TiO2-V2O5. In order to further improve the sensitivity of humidity ceramic, as well as enhance its practical usage in terms of stability, it is necessary to study the properties of humidity-sensitive ceramic with the addition of rare earth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, rare earth elements have made significant contributions to the development of high-tech industries, particularly in the field of functional ceramics. Functional ceramics can realize certain functions with direct effects and coupling effects of electricity, magnetism, sound, light, heat, and power, and have been widely used in various fields. Rare earth elements are closely related to functional ceramics, and their addition to the raw materials can significantly improve the unique functions of these ceramics, such as their agglutinating property, density, and intensity. Rare earths are used in various types of functional ceramics, such as superconducting ceramics, piezoceramics, conductive ceramics, dielectric ceramics, and sensitive ceramics. With the continuous development of technology, rare earth elements will continue to play an essential role in the advancement of functional ceramics and high-tech industries.
For more information about ceramic materials, please visit our homepage.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}
LEAVE A REPLY
SUBSCRIBE OUR NEWSLETTER
- How PBN Crucibles Ensure the Quality of GaN & SiC Epitaxial Materials
- SiC vs. Quartz Focus Rings: A Cost and Performance Analysis for Advanced Etch
- AlN Ceramic Substrates: Enabling Next-Gen Electrostatic Chucks
- The Amor of Semiconductor Tools: Why High-Purity Al2O3 & AlN Are Preferred for Plasma Process Chambers
- Silicon Carbide - Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics for Extreme Environments