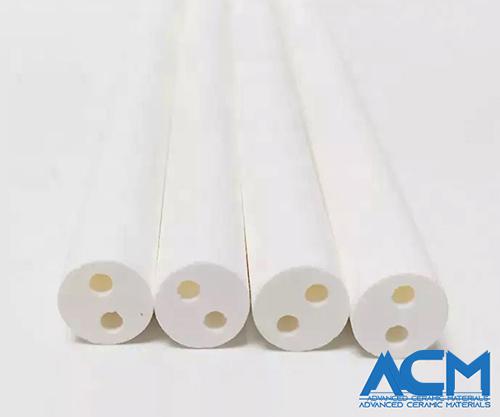
MG4425 Magnesium Oxide Insulator
- Catalog No. MG4425
- Material Magnesium Oxide
- Purity >99.0%
- Appearance White
- Bulk Density 2.3~2.5 g/cm3
Datasheet
Inquiry
MG4425 Magnesium Oxide Insulator
Magnesium Oxide Insulator Description
Magnesium Oxide Insulator serves to electrically isolate and provide mechanical support to the thermoelements of a thermocouple. With a melting point of 3098K, it boasts the highest melting point among oxides. Magnesium oxide excels in its resistance to corrosion in molten metal environments and proves to be a more versatile choice across various metals when compared to aluminum oxide.
Magnesium Oxide Insulator Specifications
|
Chemical composition (%) |
MgO |
99.8 |
99.1 |
|
CaO |
0.05 |
0.39 |
|
|
SiO2 |
0.02 |
0.29 |
|
|
Al2O3 |
0.04 |
0.13 |
|
|
Fe2O3 |
0.02 |
0.06 |
|
|
B2O3 |
<0.001 |
0.01 |
|
|
Physical properties |
Bulk density (g/cm3) |
2.3~2.5 |
|
|
Bending strength (MPa) |
20~40 |
||
Magnesium Oxide Insulator Application
Magnesium oxide (MgO) has various applications, and one of its common uses is as an insulator. Here are some key applications of magnesium oxide insulators:
-
Electrical Insulation: Magnesium oxide is widely used as an electrical insulator in power cables, transformers, and electronic devices due to its high electrical resistivity.
-
Thermal Insulation: Its excellent thermal insulation properties make magnesium oxide a crucial material in industries requiring resistance to high temperatures, such as in furnaces and thermal equipment.
-
Fireproofing: Magnesium oxide is utilized for fireproofing purposes, enhancing the fire resistance of construction materials like boards and panels.
-
Dielectric Material: It serves as a dielectric material in capacitors, contributing to the efficient storage and release of electrical energy.
-
Ceramic Insulators: Magnesium oxide is a key component in the production of ceramic insulators used in electrical equipment and power distribution systems.
Magnesium Oxide Insulator Packaging
Our Magnesium Oxide insulators are carefully handled during storage and transportation to preserve the quality of our product in its original condition.
Request a Quote
-
Attachment (Optional)
No file chosen