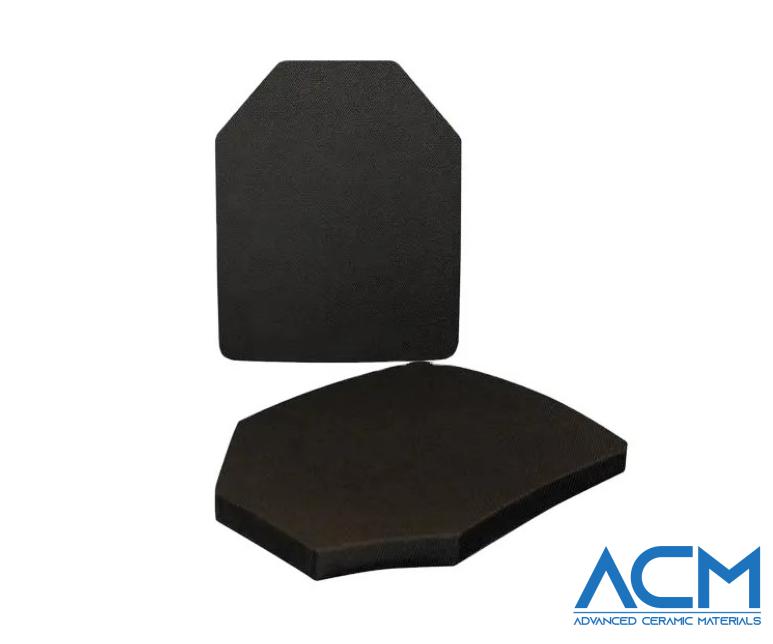
Comparison of 4 Types of Bulletproof Sheet Materials

Introduction
Bulletproof sheets are used in various applications to protect against projectiles. These sheets can absorb or deflect the impact of a bullet, reducing or preventing the penetration of the projectile. In this article, we will compare 4 types of bulletproof sheet materials based on their properties and performance. Hope that you can have a better understanding of these metals, ceramics, and aramids.
Different Bulletproof Sheet Materials
--Steel
Steel is one of the oldest and most common bulletproof sheet materials. It is durable and can provide excellent protection against most types of bullets, including handgun rounds, shotgun slugs, and even rifle rounds. The first steel armor was created by an armorer from Milan called Fillipo Negroli in 1561, and these armors were developed ever since to stop almost all bullets and shrapnel.
Although steel plates can provide a good deal of protection, they are quite heavy and bulky. With a weight of 8 to 10 pounds, steel sheet armors are dense and can be difficult to handle and transport. Therefore, civilians wearing this material may find it difficult to conceal. Steel also tends to spall, which can cause secondary injuries and can be dangerous to nearby personnel.
--Ceramic
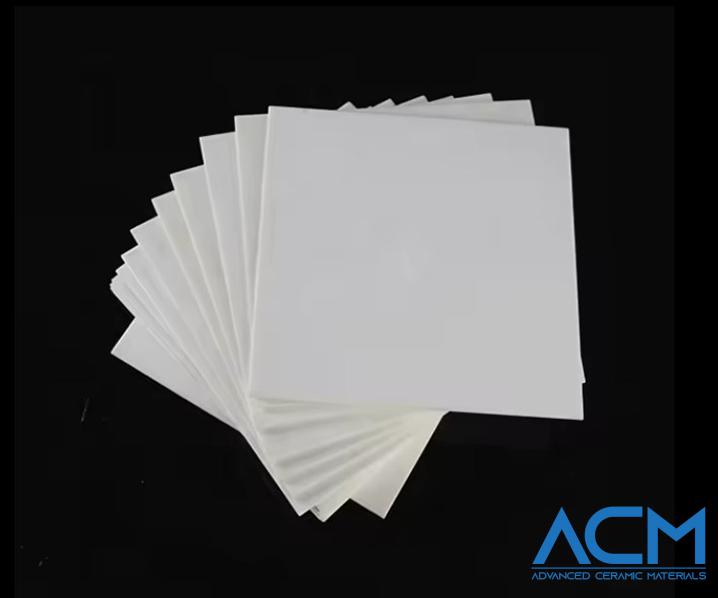
Ceramic materials, such as alumina, silicon carbide, and boron carbide, are commonly used as ballistic plates. They have a high hardness and can absorb and deflect bullets effectively. Ceramics can also be designed to break apart on impact, reducing the impact force on the wearer. These materials possess high strength, great chemical inertness, high-temperature resistance, low thermal conductivity, and high modulus of elasticity as well.
The primary benefits of ceramic sheets and plates are their low density and high-cost performance. Typically, they are about 37% lighter than steel plates and cheaper than polyethylene (PE). Additionally, they can last five to seven years if they don't take a bullet, which is a rather long time.
Nevertheless, ceramics are brittle and can crack under stress, reducing their effectiveness. They cannot withstand precision fire or heavy gunshots. Otherwise, they are prone to cracking and lost their effectiveness.
Related reading: Silicon Carbide & Boron Carbide Ceramics Used in Bulletproof Armor
--Kevlar
Kevlar is a synthetic material made from poly-para-phenylene terephthalamide fibers. It is lightweight, flexible, and has excellent impact resistance.
Kevlar is a type of aramid. This material lowers the overall weight and improves the mobility of the person wearing the armor consequently. Also, Kevlar has outstanding durability, flexibility, and strength because of its powerful chemical bonds. With these features, Kevlar is commonly used in body armor and is effective against most handgun rounds.
Yet, it is less effective against high-velocity rifle rounds. Kevlar armors only work for low to medium-velocity weapon rounds. So please add steel, UHMWPE, or ceramic materials in your armors if you are going to face heavy fire. Besides, Kevlar can be damaged by ultraviolet rays, excessive washing, and dry washing, so special care and caution are needed.
--UHMWPE
Ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE), shortened as polyethylene, or PE, is a lightweight synthetic material that has excellent impact resistance.
This lightweight but strong material can prevent against most handgun rounds. A plate made from PE generally weighs just 2 to 5 pounds, providing greater comfort for the wearer. Another glowing benefit of PE is that it is 15 times stronger than steel. UHMWPE is also resistant to UV radiation and water, making it ideal for use in harsh environments.
But, UHMWPE can be expensive and tends to degrade over time. PE armor is a rather expensive option due to its costly composition and manufacturing process. PE plates are 200%-300% more expensive than ceramic or steel. They also show lower tolerance when above 158 F, which is not effective in deserts and other hot regions
You can check the table below for more information.
Table 1. Comparison of Bulletproof Sheet Materials
|
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Steel |
Durable; Good protection against most types of bullets ; |
Heavy; Hard to conceal; Prone to spall; |
|
Ceramic |
Light and strong; Effective at absorbing bullets; |
Brittle; Crack under stress; |
|
Kevlar |
Light and flexible; Good against most handguns; |
Not effective against high-velocity rifle rounds; |
|
UHMWPE |
Light and resistant to UV, etc. |
Expensive; |
Conclusion
In a word, steel, ceramic, Kevlar, and UHMWPE are all viable options for bulletproof sheet materials, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Steel is durable but heavy, ceramic materials are hard but brittle, Kevlar is lightweight but less effective against high-velocity rifle rounds, and UHMWPE is lightweight but can be expensive. The choice of material depends on the specific application and desired level of protection.
Advanced Ceramic Materials (ACM) offers impressive bulletproof materials at competitive prices. We have performance alumina, silicon carbide, and boron carbide ceramics of good quality in different forms and shapes. For further details about bulletproof ceramic sheets and plates, please check our homepage.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}
LEAVE A REPLY
SUBSCRIBE OUR NEWSLETTER
- How PBN Crucibles Ensure the Quality of GaN & SiC Epitaxial Materials
- SiC vs. Quartz Focus Rings: A Cost and Performance Analysis for Advanced Etch
- AlN Ceramic Substrates: Enabling Next-Gen Electrostatic Chucks
- The Amor of Semiconductor Tools: Why High-Purity Al2O3 & AlN Are Preferred for Plasma Process Chambers
- Silicon Carbide - Ultra-High Temperature Ceramics for Extreme Environments