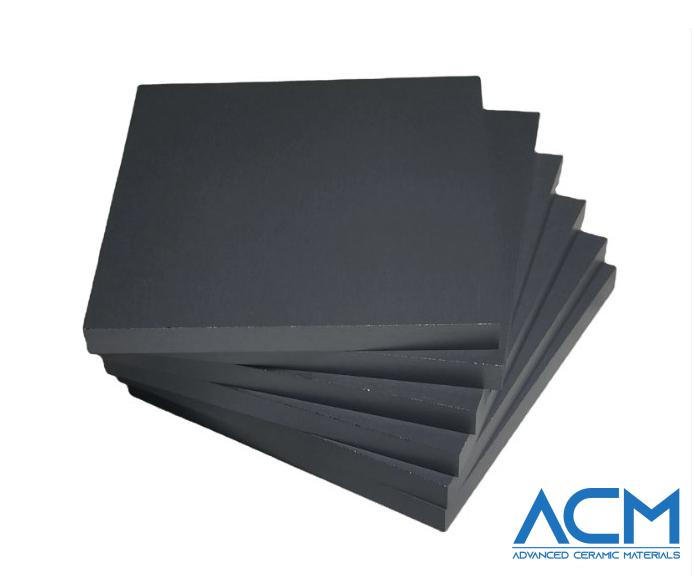
CA0912 Boron Carbide Plate, B4C Plate
- Catalog No. CA0912
- Molecular Formula B4C
- Appearance Black
- Melting Point 2445℃
- Density 2.1 to 2.7 g/cm3
- Poisson's Ratio 0.17-0.18
- Specific Heat 950 J/kg-K
- Tensile Strength 350 MPa (Ultimate)
CA0912 Boron Carbide Plate, B4C Plate
Description
Advanced Ceramic Materials (ACM) offers high-quality Boron Carbide Plates, known for their exceptional hardness and strength. Boron Carbide (B4C) is one of the hardest materials, discovered in 1899, with a Mohs hardness of about 9.49, making it the third hardest material after diamond and cubic boron nitride. This remarkable hardness, combined with high strength, low density, corrosion resistance, high-temperature resistance, low thermal conductivity, and high modulus of elasticity, makes Boron Carbide ideal for various applications.
Technical Data
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Mohs Hardness | 9.49 |
| Density | 2.1 to 2.7 g/cm³ |
| Melting Point | 2445 °C |
| Electrical Resistivity | 0 to 11 x 10^3 Ω-m |
| Poisson's Ratio | 0.17-0.18 |
| Specific Heat | 950 J/kg-K |
| Tensile Strength (Ultimate) | 350 MPa |
| Thermal Conductivity | 31 to 90 W/m-K |
| Thermal Expansion | 4.5 to 5.6 µm/m-K |
Key Features and Benefits
- Exceptional Hardness: Mohs hardness of 9.49, third hardest material after diamond and cubic boron nitride.
- Lightweight: Despite its high hardness and strength, Boron Carbide is lightweight, making it ideal for personal and vehicle armor.
- High Wear Resistance: Excellent wear and abrasion resistance.
- High Temperature Resistance: Can withstand extremely high temperatures.
- Chemical Resistance: Resistant to chemical attacks, making it suitable for various industrial applications.
Applications
Boron Carbide Plates are used in various applications, including:
- Abrasive Field: Used for surfaces of watches and jewels due to its high wear resistance.
- Refractory Materials: Acts as an antioxidant additive in refractory materials.
- Ceramic Materials: Ideal for wear-resistant components used in blasting, sealing, machinery, ships, automotive, dies, aviation, and aerospace industries.
- Armor Tiles: Used in high-density armor tiles and bulletproof seats of helicopters for superior ballistic protection.
- Nuclear Industry: Important material for nuclear applications due to its high absorption cross-section.
- Boriding Agent: Used as a raw material in boriding agents to improve surface hardness and wear resistance.
- Chemical Additives: Produces other boron-containing materials such as titanium boride or zirconium boride.
- Solid Fuel: Used in boron carbide-based propellants for ducted rockets.
Packaging and Quality Assurance
ACM’s Boron Carbide Plates are carefully handled to minimize damage during storage and transportation, ensuring the products remain in their original high-quality condition. Various types of ceramic plates come in different sizes and offer different levels of protection. Please contact us for more information.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is the maximum operating temperature for Boron Carbide plates?
- Our Boron Carbide plates can withstand temperatures up to 2445°C.
-
Do you offer custom sizes and shapes?
- Yes, we offer custom sizes and shapes to meet specific requirements. Please contact us for more details.
-
What are the typical applications for Boron Carbide Plates?
- Boron Carbide plates are used in the abrasive field, refractory materials, ceramic materials, armor tiles, the nuclear industry, boriding agents, chemical additives, and solid fuel.
Discover More
- Other Boron Carbide Products: Explore our range of boron carbide products.
- Latest Post: Read our latest article on Boron Carbide Applications.
- Contact Us: Get in touch or request a quote for more information.
-
Attachment (Optional)
No file chosen