High-Performance Ceramics on Bulletproof Plates: SiC, BN, B4C and Al2O3
Introduction
Effective personal protection is paramount today, especially for military and law enforcement personnel. One of the critical components in modern protective gear is the bulletproof plate, which plays a vital role in stopping projectiles and mitigating injuries. Among the various materials used for this purpose, high-performance ceramics stand out due to their exceptional hardness, lightweight nature, and durability.
This article delves into four prominent ceramics used in bulletproof plates: Silicon Carbide (SiC), Boron Nitride (BN), Boron Carbide (B4C), and Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3). We will explore their unique properties, applications, advantages, and comparative performance to understand why these materials are integral to modern armor technology.
1. Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Silicon Carbide (SiC) is renowned for its impressive hardness and thermal stability, making it an excellent material for bulletproof armor. SiC's crystalline structure provides high resistance to mechanical stresses and thermal shock. This ceramic material is particularly valued in situations requiring lightweight yet highly durable armor solutions.
Properties:
- Hardness: SiC is one of the hardest ceramics available, which translates to high resistance against penetration.
- Density: It has a relatively low density, contributing to lighter armor that does not compromise mobility.
- Thermal Stability: Exceptional performance under high temperatures, which is crucial during high-velocity impacts.
Applications: SiC is widely used in military and civilian ballistic protection due to its ability to absorb and dissipate the energy of incoming projectiles. Its application ranges from personal body armor to vehicle protection and aircraft armor.
Advantages:
- High hardness and toughness
- Lightweight compared to metals
- Excellent thermal resistance
Disadvantages:
- Higher cost compared to some other ceramics
- Brittle nature can lead to catastrophic failure under certain conditions
Comparative Performance: Compared to other ceramics, SiC offers a balanced combination of lightness and hardness, making it a preferred choice for advanced armor systems where weight is a critical factor.
2. Boron Nitride (BN)
Boron Nitride (BN) is another high-performance ceramic used in bulletproof armor. Known for its exceptional thermal conductivity and chemical stability, BN provides a unique set of properties that make it suitable for ballistic protection.
Properties:
- Thermal Conductivity: BN has excellent thermal conductivity, which helps in dissipating heat generated upon impact.
- Chemical Stability: It is highly resistant to chemical attack, ensuring durability in various environments.
- Hardness: Though not as hard as SiC or B4C, BN still offers considerable hardness for ballistic applications.
Applications: BN is often used in composite armor systems where its thermal properties are particularly advantageous. It can be found in personal protective equipment and vehicle armor, enhancing the overall performance of these systems.
Advantages:
- Superior thermal management
- Chemical and thermal stability
- Lightweight
Disadvantages:
- Lower hardness compared to SiC and B4C
- Can be more expensive than other ceramic materials
Comparative Performance: While BN may not be the hardest ceramic, its thermal properties make it a valuable component in armor systems designed to manage the heat generated during ballistic impacts.
3. Boron Carbide (B4C)
Boron Carbide (B4C) is one of the hardest known materials, second only to diamond, making it an excellent choice for bulletproof applications. Its combination of extreme hardness and low density makes B4C highly effective in stopping high-velocity projectiles.
Properties:
- Hardness: Extremely hard, providing superior protection against penetration.
- Density: Very low density, making it ideal for lightweight armor systems.
- Neutron Absorption: B4C also has the unique property of absorbing neutrons, adding an extra layer of protection in nuclear environments.
Applications: B4C is used in a variety of ballistic protection applications, including personal body armor, vehicle armor, and protective inserts for military and law enforcement personnel.
Advantages:
- Exceptional hardness and durability
- Very lightweight
- Neutron absorption capabilities
Disadvantages:
- Brittle and can fracture under extreme stress
- Higher cost compared to other ceramics
Comparative Performance: B4C stands out for its hardness and lightness, making it one of the most effective materials for bulletproof armor. However, its brittleness requires careful engineering to avoid catastrophic failure.
4. Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3)
Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3), commonly known as alumina, is a widely used ceramic in bulletproof applications. It offers a good balance of hardness, wear resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for various protective solutions.
Properties:
- Hardness: High hardness, though not as high as SiC or B4C.
- Wear Resistance: Excellent wear resistance, extending the life of armor plates.
- Cost-Effectiveness: More affordable than SiC and B4C, making it accessible for broader applications.
Applications: Al2O3 is extensively used in body armor, vehicle armor, and other protective gear. Its cost-effectiveness allows for widespread use in both military and civilian protection systems.
Advantages:
- High hardness and wear resistance
- Cost-effective compared to other high-performance ceramics
- Reliable and widely available
Disadvantages:
- Heavier than SiC and B4C
- Slightly lower performance in extreme conditions
Comparative Performance: Al2O3 provides a good balance between cost and performance, making it suitable for a wide range of applications where budget constraints are a factor.
Comparative Analysis
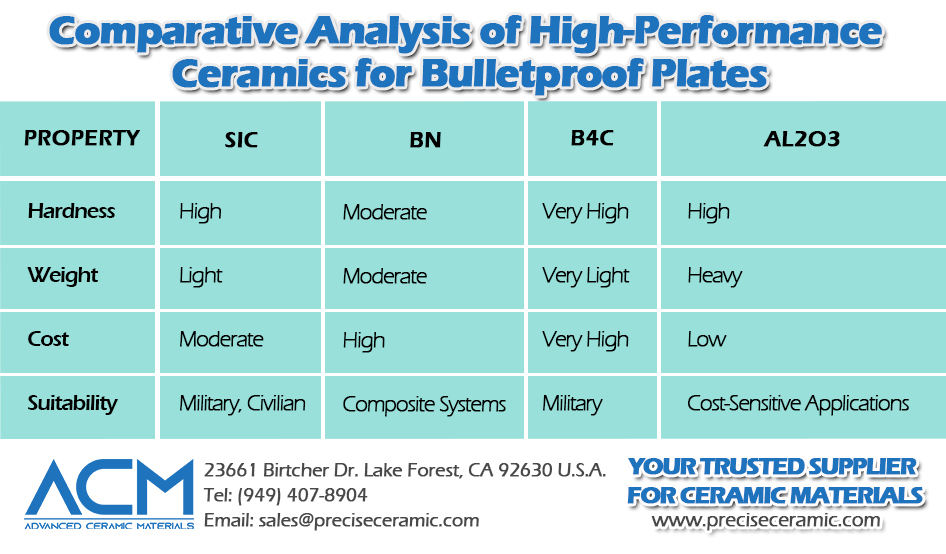
When comparing SiC, BN, B4C, and Al2O3, several factors come into play, including hardness, weight, cost, and specific application needs.
- Hardness: B4C > SiC > Al2O3 > BN
- Weight: B4C and SiC are lighter compared to Al2O3 and BN.
- Cost: Al2O3 is the most cost-effective, while B4C is the most expensive.
- Suitability: SiC and B4C are preferred for high-performance military applications, whereas Al2O3 is often used in cost-sensitive scenarios. BN, with its thermal properties, is ideal for composite systems requiring efficient heat management.
Conclusion
High-performance ceramics play a crucial role in modern bulletproof armor, offering a range of properties that make them ideal for various protective applications. SiC, BN, B4C, and Al2O3 each have unique strengths and weaknesses, making them suitable for different scenarios. Advanced Ceramic Materials (ACM), a leading supplier of advanced ceramics, provides these materials to ensure the highest level of protection for military and civilian use. As research and technology continue to advance, the effectiveness and application of these materials are expected to improve, providing even better protection for those who need it most.
{{item.content}}
LEVE A REPLY
{{item.children[0].content}}
{{item.content}}
LEAVE A REPLY
SUBSCRIBE OUR NEWSLETTER
- Boron Nitride in Cosmetics: Enhancing Performance and Sensory Appeal
- Maximize MOCVD Yield and Purity with Hexagonal Boron Nitride Setters
- What Are the Advantages and Uses of Boron Nitride Ceramic Sheet?
- The Compression Annealing Advantage for Pyrolytic Boron Nitride
- Beyond Insulation: The Surprising Spectrum of Ceramic Thermal Conductivity